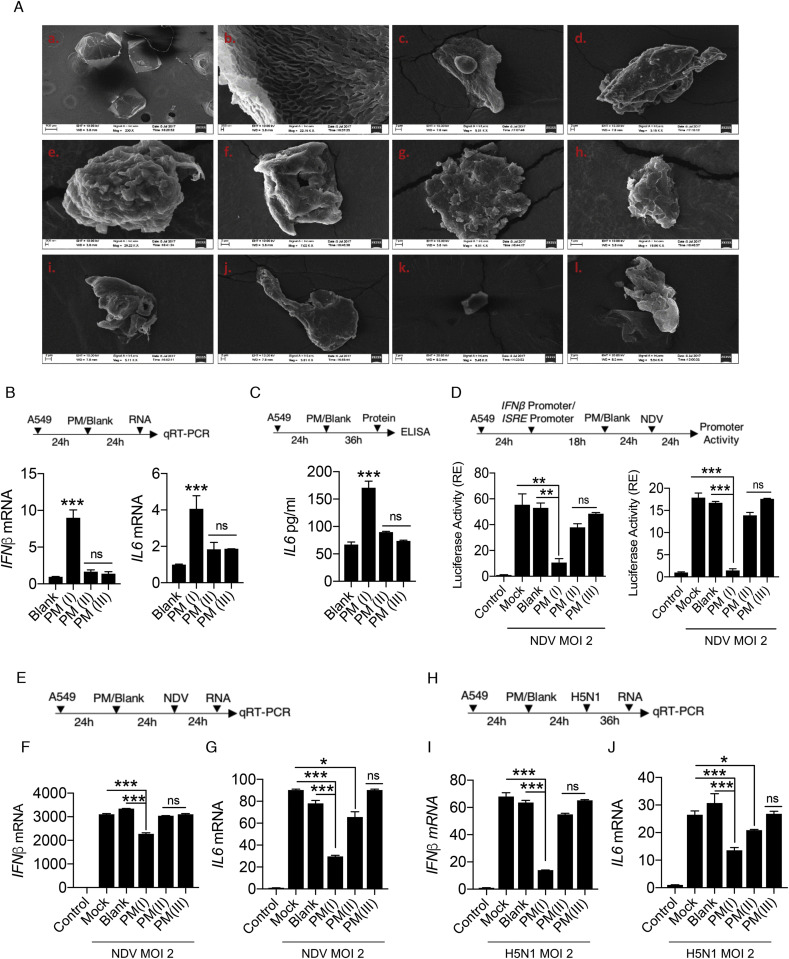
Fig. 1.
PM10regulates the innate immune response upon RNA virus infection – (A) Scanning electron images of coarse airborne particulate matter PM10. (a) Image of blank (control) solution with no PM10 dissolved in it. (b–l) Images of different shapes with varied structures representing the different characteristic morphological features of PM10 in the samples. Quantification of innate immune response. A549 cells were treated with PM10 (at different dosage: PM(I), PM(II), and PM(III) – details are mentioned in the methods section) and control mentioned as blank for (B) 24 h then harvested in Trizol to quantify the mRNA expression of IFNβ and IL6 by qRT-PCR. (C) 36 h then cell supernatant was collected to measure the protein level of IL6 by ELISA. (D) Schematic representation of workflow for quantification of IFNβ and ISRE promoter activities by luciferase assay as indicated in A549 cells. NDV represents New-Castle Disease Virus infection at MOI = 2. (E) Schematic work flow of PM10 exposure (at different dosage: PM(I), PM(II), and PM(III) – details are mentioned in the methods section) and NDV infection. (F–G) Quantification of IFNβ and IL6 mRNA transcripts in uninfected (control), mock infected, blank treated and PM10 exposed cells by qRT-PCR. (H) Schematic work flow of PM10 (at different dosage: PM(I), PM(II), and PM(III) – details are mentioned in the methods section) exposure and H5N1 Influenza infection. (I–J) Quantification of IFNβ and IL6 mRNA transcripts in uninfected (control), mock infected, blank treated and PM10 exposed cells by qRT-PCR. Data are mean ± SEM of triplicate samples from single experiment and are representative of three independent experiments. ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗p < 0.01 and ∗p < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA Tukey test and unpaired t-test.