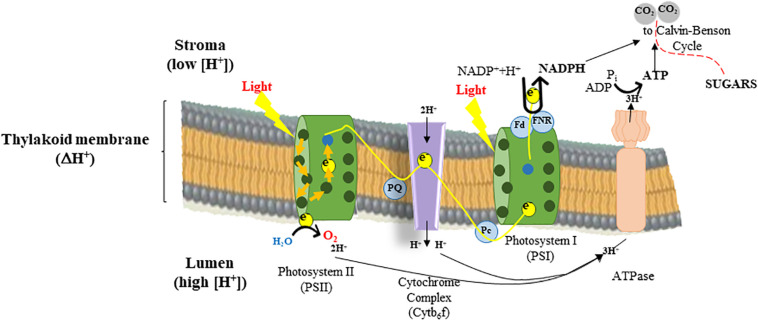
FIGURE 2.
Light energy drives mainstream electron flow used by photosystem II (PSII) to reduce plastoquinone (PQ) to plastoquinol. The reducing equivalents on plastoquinol move through the electron transfer chain (ETC) to the cytochrome b6f complex and plastocyanin (Pc), releasing protons (H+) into the thylakoid lumen, while the electrons are used by photosystem I (PSI) to reduce ferredoxin (Fd), again driven by light-supported ETC through PSI. Reduced Fd is coupled to Fd:NADP(H) oxidoreductase (FNR) that catalyzes the reduction of NADP+ to NADPH. The oxidation of water by PSII and the oxidation of plastoquinol by the cytochrome b6f complex allows the generation of a ΔpH between the thylakoid lumen and the stroma, essential for generating ATP via the ATPase and balancing the proportion of ATP:NADPH produced by electron transfer that is required to function the Calvin cycle that assimilates CO2 and leads to sugar production, and plant growth.