Figure 1.
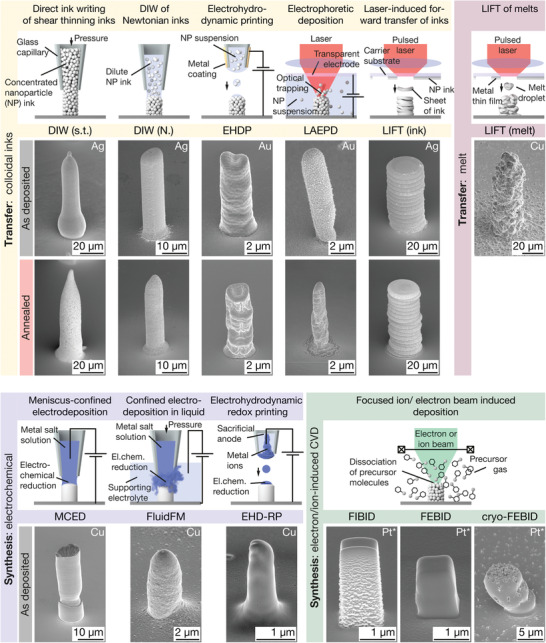
Small‐scale metal AM methods included in this study and pillars printed by these techniques. Small‐sale AM methods are grouped into transfer and synthesis methods, based on their principle of metal deposition. Subgroups include: Transfer of colloids, transfer of melts, electrochemical synthesis and synthesis via electron/ion‐induced CVD. The SE micrographs show representative pillars printed with each of the techniques tested in this study. As‐printed and annealed pillars are shown if thermal annealing was performed (not the same samples). Samples for DIW and LIFT (ink) are printed from Ag inks, and samples from EHDP and LAEPD from suspensions of Au nanoparticles. The LIFT (melt) pillar is Cu (for Au, see Figure S1, Supporting Information), as are the structures for MCED, the FluidFM and EHD‐RP. FIBID and (cryo‐)FEBID pillars were deposited from Methylcyclopentadienyl platinum (IV) trimethyl (MeCpPt(Me)3). *: Pt nanoparticles embedded in a carbonaceous matrix. Tilt angle of all micrographs: 55°.
