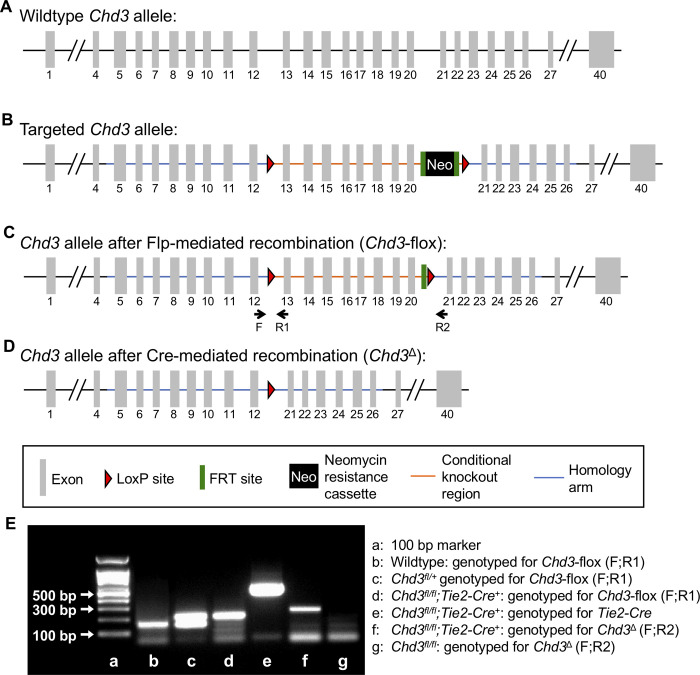
Fig 1. Generation of a conditional murine Chd3 knockout allele.
The Chd3-flox allele was generated using homologous recombination of a targeting vector in C57Bl/6 embryonic stem cells. (A): The wildtype murine Chd3 allele contains 40 exons and resides on chromosome 11. (B): The targeting vector incorporated a 5’ LoxP site (red triangle) inserted between exons 12 and 13 and a 3’ LoxP site inserted between exons 20 and 21 of the wildtype Chd3 allele. In addition, a neomycin resistance (Neo) cassette flanked by Frt sites (green bars) was inserted immediately upstream of the 3’ LoxP site for positive selection of the integrated targeting vector. (C): The Neo cassette was removed by crossing mice carrying the targeted allele to FLPe-recombinase mice, leaving a single Frt site upstream of the 3’ LoxP site in the Chd3-flox allele after recombination. Genotyping primers are indicated below the allele. (D): After crossing mice carrying the Chd3-flox allele to a line carrying a Cre recombinase, exons 13–20 were deleted (Chd3Δ). (E): The indicated mice were genotyped by PCR using the primers shown in parentheses and diagrammed in (C) to demonstrate targeting and Cre-mediated excision of the Chd3-flox allele. PCR products were run on a 2% agarose gel. See Table 1 for primer sequences and predicted amplicon sizes.