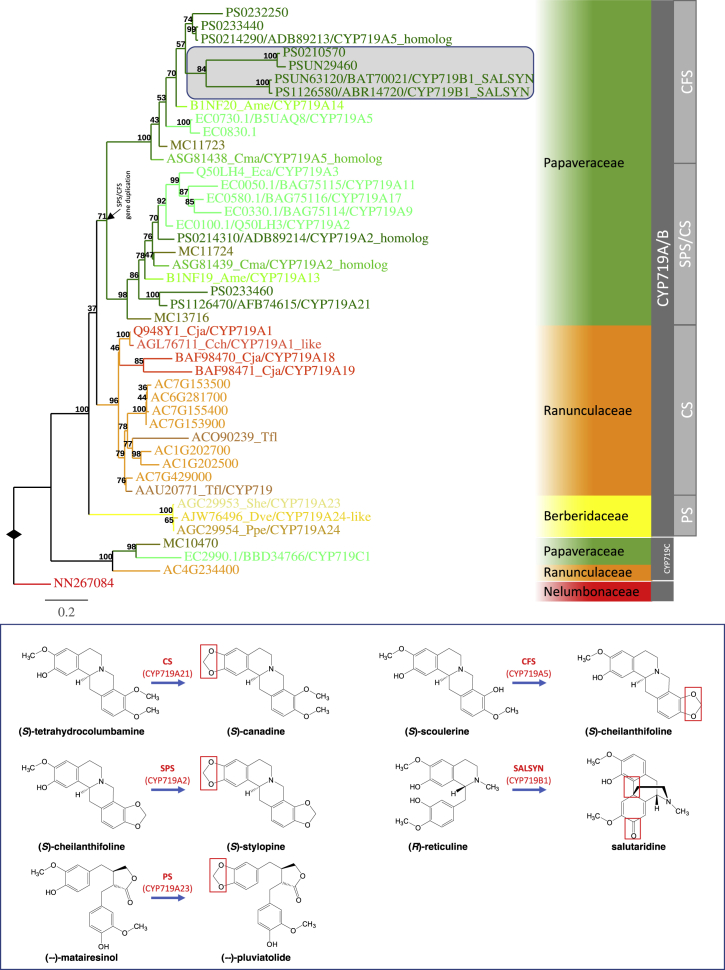
Figure 4.
CYP719 Tree Analysis Suggests Key Duplication Events for the Evolution of Multiple BIA Biosynthetic Pathways.
All functionally characterized CYP719 proteins fall into the CYP719A/B clade, which contains sequences exclusively from Ranunculales species. The CYP719A/B clade contains several strongly supported subclades. The CS subclade contains sequences exclusively from Ranunculaceae species, and all of its functionally characterized members exhibit CS activity. Both the SPS/CS and CFS subclades consist of sequences exclusively from Papaveraceae species. All functionally characterized SPS proteins fall into the SPS/CS subclade, whereas all functionally characterized CFS proteins are members of the CFS subclade. The SPS/CS subclade also contains the opium poppy CS sequence CYP719A21, and the trifunctional (S)-canadine synthase/(S)-stylopine synthase/(S)-nandinine synthase (CYP719A13) from Argemone mexicana. SALSYN (CYP719B1) falls into an opium poppy group inside the CFS subclade highlighted by the shaded box in the tree. The figure descriptors and legends are in the same format as described in Figure 3. Extended information of the gene tree is included in Supplemental Information. The black arrow indicates the occurrence of the gene-duplication event giving rise to SPP/CFS. The inset shows the reactions catalyzed by functionally characterized members of the CYP719 subfamily with the reactive groups highlighted in red boxes.