Figure 9.
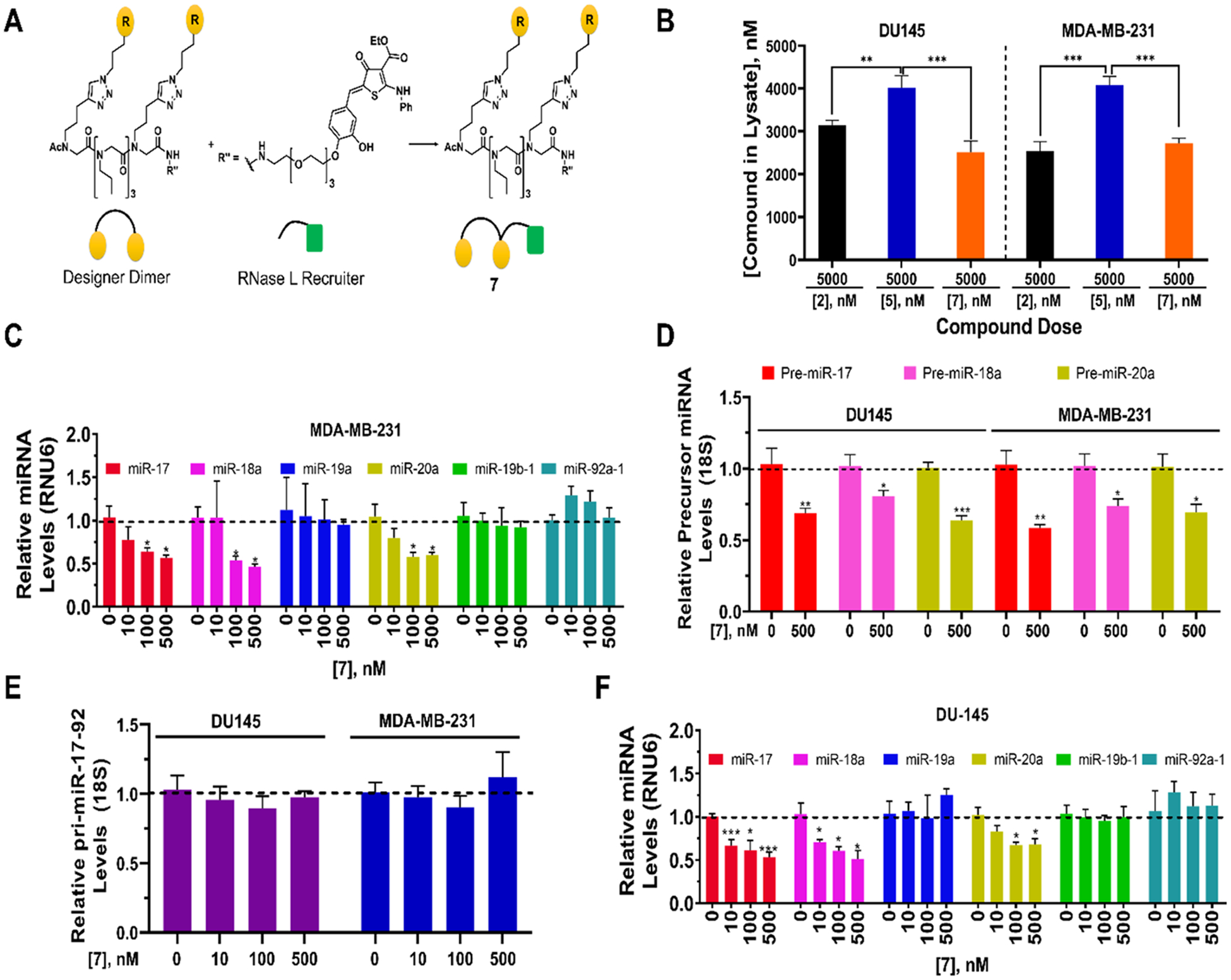
Bioactivity of RIBOTAC 7 in MDA-MB-231 TNBC and DU-145 prostate cancer cells. (A) Structure of RIBOTAC 7, generated by coupling dimer binder 2 with a small molecule that recruits RNase L discovered previously.57 (B) Cellular permeability of 2 (dimer binder), 5 (dimer-bleomycin conjugate) and RIBOTAC 7 at 5 μM. (C) Effect of 7 on the levels of mature miRNAs from the 17–92 cluster in MDA-MB-231 TNBC cells, as determined by RT-qPCR. (D) Effect of 7 on pre-miR-17, −18a, and −20a levels in MDA-MB-231 and DU-145 cells, as determined by RT-qPCR. (E) Effect of 7 on pri-miR-17–92 in MDA-MB-231 TNBC and DU-145 prostate cancer cells, as determined by RT-qPCR. (F) Effect of 7 on the levels of mature miRNAs from the 17–92 cluster in DU-145 prostate cancer cells, as determined by RT-qPCR. *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01, ***, p < 0.001 by a Student t test. All errors are reported as SEM.
