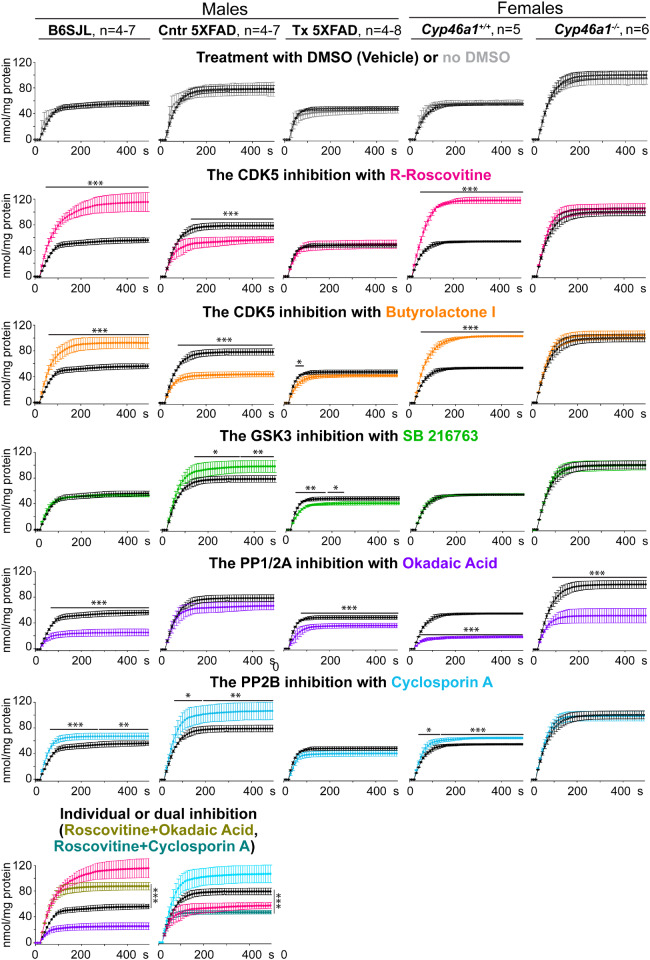
Figure 6.
Effects of protein kinase and protein phosphatase inhibition on KCl-induced glutamate (Glu) release. Traces of the KCl-induced Glu release after synaptosomal fractions were incubated with or no DMSO (black and grey traces, respectively), R-roscovitine (magenta traces), butyrolactone I (orange traces), SB 216763 (green traces), okadaic acid (ink traces) and cyclosporin A (blue traces) or co-inhibited with R-roscovitive plus okadaic acid (olive traces) and R-roscovitive plus cyclosporin A (teal traces). All traces are the mean ± SD of the measurements in individual animals (n = 4–8 mice per group and gender). Statistical analysis: a two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc comparisons. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001. B6SJL, mice on the B6SJL background; Cntr, control or vehicle-treated 5XFAD mice, and Tx, EFV-treated 5XFAD mice on the B6SJL background; Cyp46a1+/+ and Cyp46a1−/−, wild-type and knockout mice on the C57BL/6J; 129S6/SvEv background.