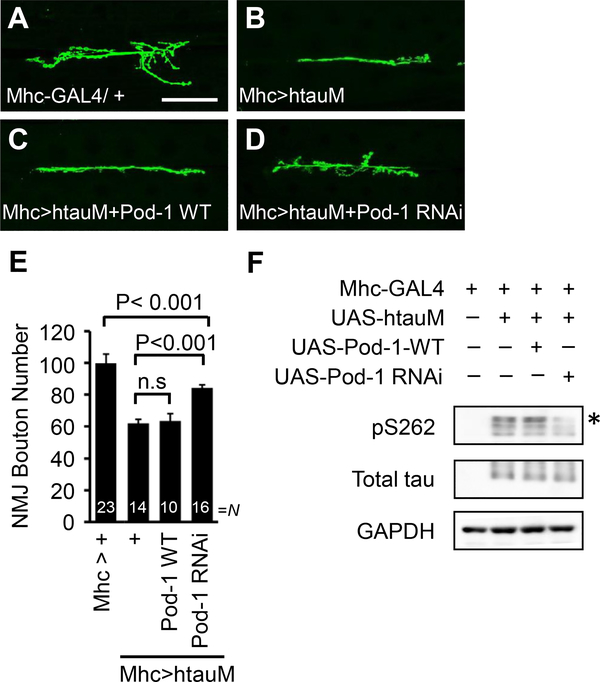
Fig. 5.
Pod-1 knockdown reduces synaptic toxicity caused by htauM. (A–D) The interaction between Pod-1 and htauM in the Drosophila NMJ. Representative NMJ terminals of the indicated genotypes were shown by anti-HRP immunostaining. The genotypes are Mhc-Gal4>+ (A), Mhc-Gal4>UAS-htauM (B), Mhc-Gal4>UAS-htauM+UAS-Pod-1-WT (C) and Mhc-Gal4>UAS-htauM+UAS-Pod-1 RNAi (D). Scale bar (AeD), 50 μm. (E) Quantification of data showing phenotypic interaction between htauM and Pod-1 on the total number of boutons per muscle area on muscle 6/7 of A3. N indicates the number of animals analyzed in each group. Statistical significance was determined pair-wise using a two-tailed Student’s t-test. n.s, not significant. (F) Western blot analysis of pTau S262 and total tau after coexpression of Pod-1-WT and Pod-1 RNAi in an Mhc-GAL4>UAS-htauM background. The pTau S262 level in larval muscle wall extracts was increased by Pod-1-WT, whereas it was decreased by Pod-1 RNAi compared to control. pTau S262 proteins marked with an asterisk. GAPDH serves as a loading control.