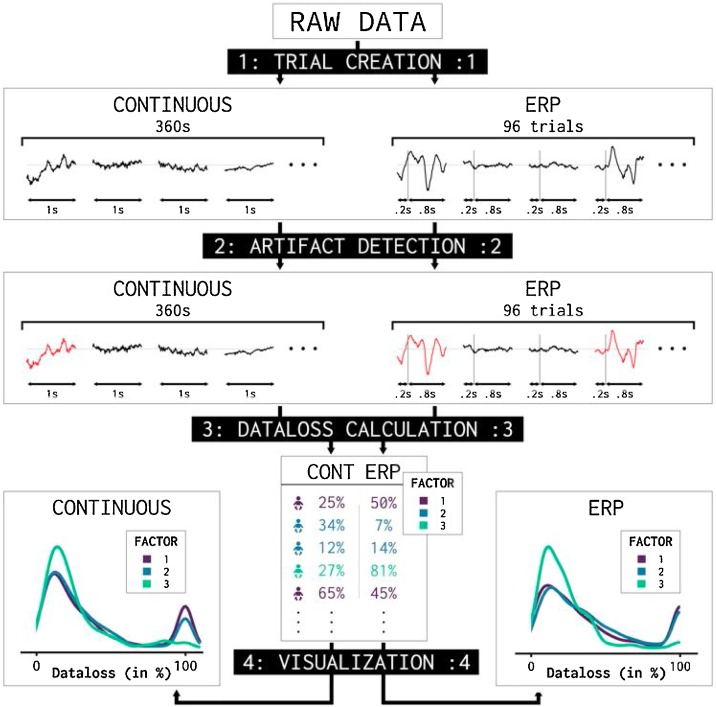
Fig. 1.
Graphical overview of analysis design. Data is analyzed in four steps. 1) Raw data is cut into 1 s trials for both the continuous and ERP task, resulting in 360 and 96 trials respectively. 2) Jump, noise and flatline artifacts are detected and trials containing artifacts are selected. 3) Data loss is calculated by calculating the percentage of trials containing artifacts over the total expected trials (360 in the case of the continuous experiment and 96 in the case of the ERP experiment). 4) Subjects are grouped based on factor and the data loss distributions are visualized using a probability density function. The probability density functions plotted in the visualization step are made using the gramm toolbox (Morel, 2018). The stat_density.m function is based on the standard ksdensity.m function in matlab.