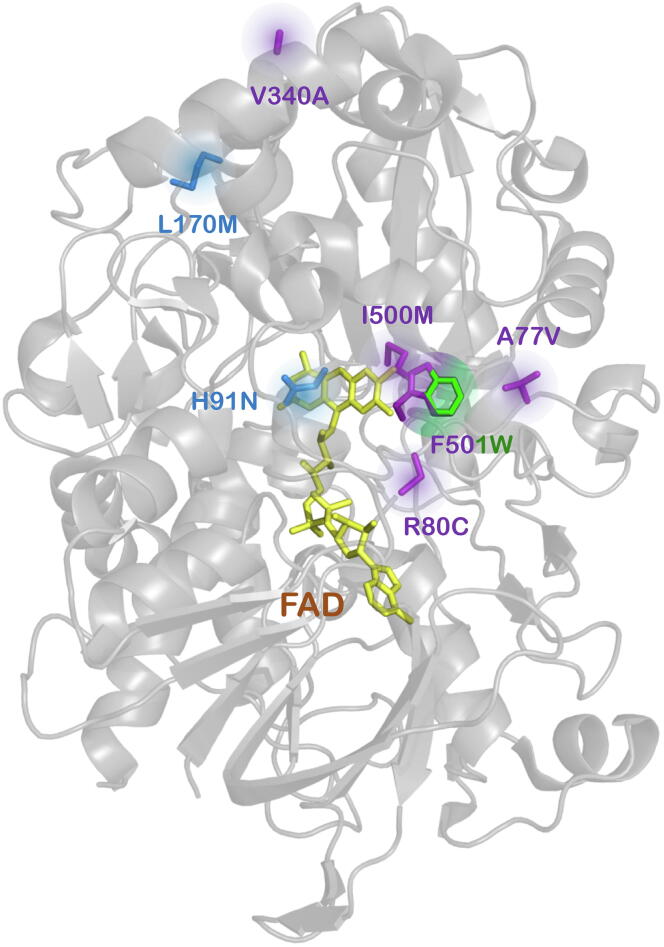
Fig. 6.
The mutations identified in AAO throughout the directed evolution campaigns. FAD is depicted in yellow and the catalytic histidine residues in red. The mutations corresponding to the evolution of secretion are indicated in blue, and those for the evolution of secondary alcohol oxidation are in purple, while mutations corresponding to furfural derivative oxidations are depicted in green. Substitution F501W, from two evolution campaigns, is depicted in both purple and green. Note that the H91N mutation enhances substrate promiscuity in the FDCA route. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)