Figure 3.
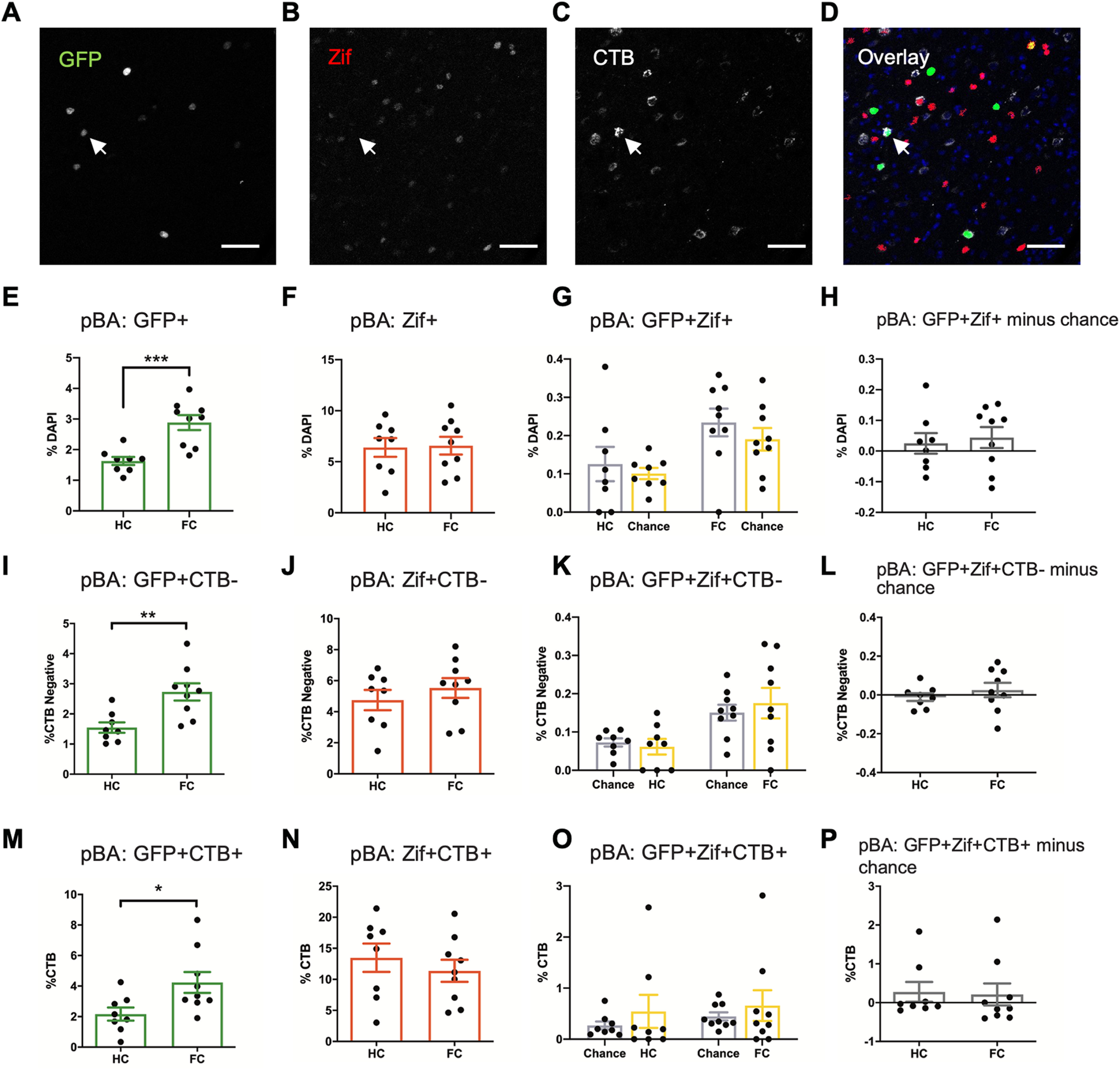
The pBA-dBNST circuit is active during contextual fear conditioning, but is not incorporated into the fear engram. A–D, Representative images of GFP, Zif, CTB, and overlay from a section of pBA with DAPI (blue). White arrow indicates a GFP+Zif-CTB+ cell. Scale bar = 50 μm. E, Contextual fear conditioning increased the percentage of GFP+ neurons among DAPI cells in the pBA (p = 0.0005). F, There was no difference between FC and HC in total percentage of Zif+ neurons in the pBA (p = 0.89) due to fear retrieval. G, Fear conditioning and retrieval did not increase the percentage of GFP+Zif+ reactivated fear neurons compared with chance level in the pBA (p = 0.23). H, The number of GFP+Zif+ cells minus chance level was not significantly different in the FC group compared with HC in the pBA (p = 0.70). I–L, Fear conditioning increased levels of GFP+ in the CTB– population in the pBA, but Zif+ and GFP+Zif+ did not differ between the groups; E, GFP+CTB– (p = 0.0036); F, Zif+CTB– (p = 0.41); G, GFP+Zif+CTB– versus chance (HC: p = 0.58; FC: p = 0.52); H, GFP+Zif+CTB– cells minus chance (p = 0.42). M–P, Fear conditioning increased levels of GFP+ in the CTB+ population in the pBA, but Zif+ and GFP+Zif+ did not differ between the groups; M, GFP+CTB+ (p = 0.025); N, Zif+CTB+ (p = 0.47); O, GFP+Zif+CTB+ versus chance (HC: p = 0.84; FC: p = 0.82); P, GFP+Zif+CTB+ cells minus chance level (p = 0.48). Graphs show mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
