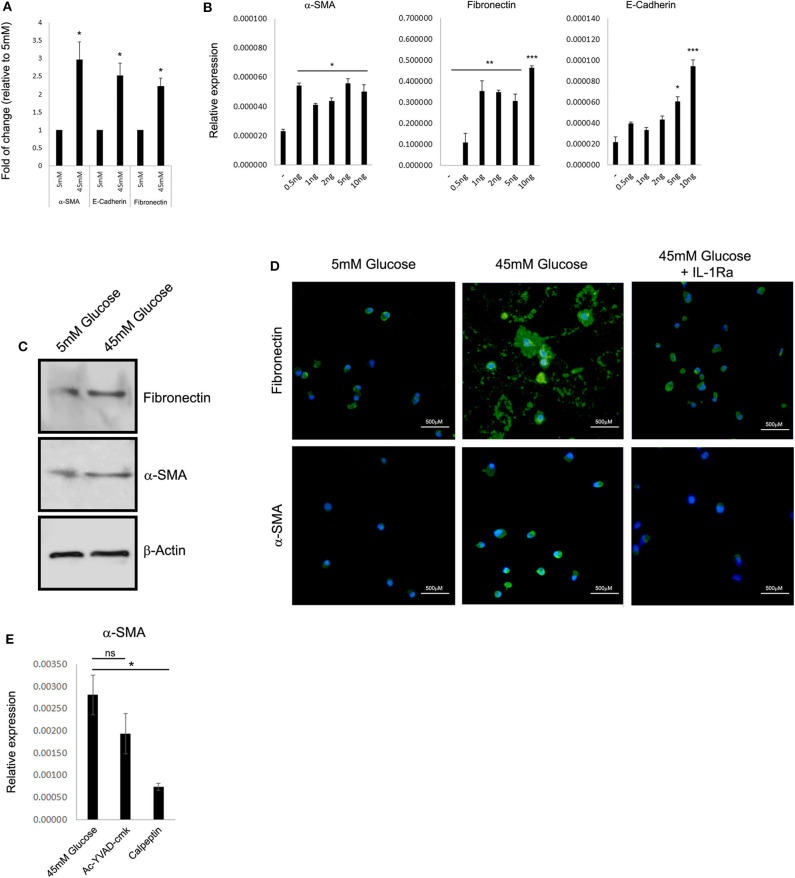
Figure 2.
High glucose leads to IL-1α-dependent expression of extracellular matrix proteins in renal tubular epithelial cells. (A) HK-2 human proximal tubular kidney cells were exposed to different glucose concentrations for 48 h. The expression of the EMC genes α-SMA, E-cadherin, and fibronectin was evaluated using qPCR and was normalized relative to the expression of the housekeeping gene β-actin. Results are expressed as fold of change relative to the control of low glucose concentration (5 mM). (B) Gradual increasing concentrations of recombinant human IL-1α (rhIL-1α) were added to quiescent HK-2 cells in 5 mM low glucose. The expression of the EMC genes α-SMA, E-cadherin, and fibronectin was evaluated using qPCR as in panel (A) after 24 h. Data are expressed as normalized relative expression to β-actin. (C) Western blot of whole-cell proteins assessing the cell-associated levels of the EMC proteins α-SMA and fibronectin after exposer of HK-2 cells to low (5 mM), high glucose (45 mM). (D) Representative immunofluorescence snapshots of HK-2 cells in low (5 mM), HG (45 mM), or HG with rhIL-1α (10 ng/mL). Designated antibodies were used to detect the intracellular or extracellular localization and expression levels of the ECM proteins fibronectin and α-SMA. Green: fibronectin; yellow: α-SMA; and blue: DAPI; white lines show 500-μm bars. Note that the extracellular staining is the deposition of ECM proteins (fibronectin, middle panel). (E) HK-2 cells were exposed to HG for 48 h with or without the presence of Ac-YVAD-cmk (50 μM) or calpeptin (20 μM). The expression of α-SMA was monitored using qPCR as in panel (A). t test p values: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.