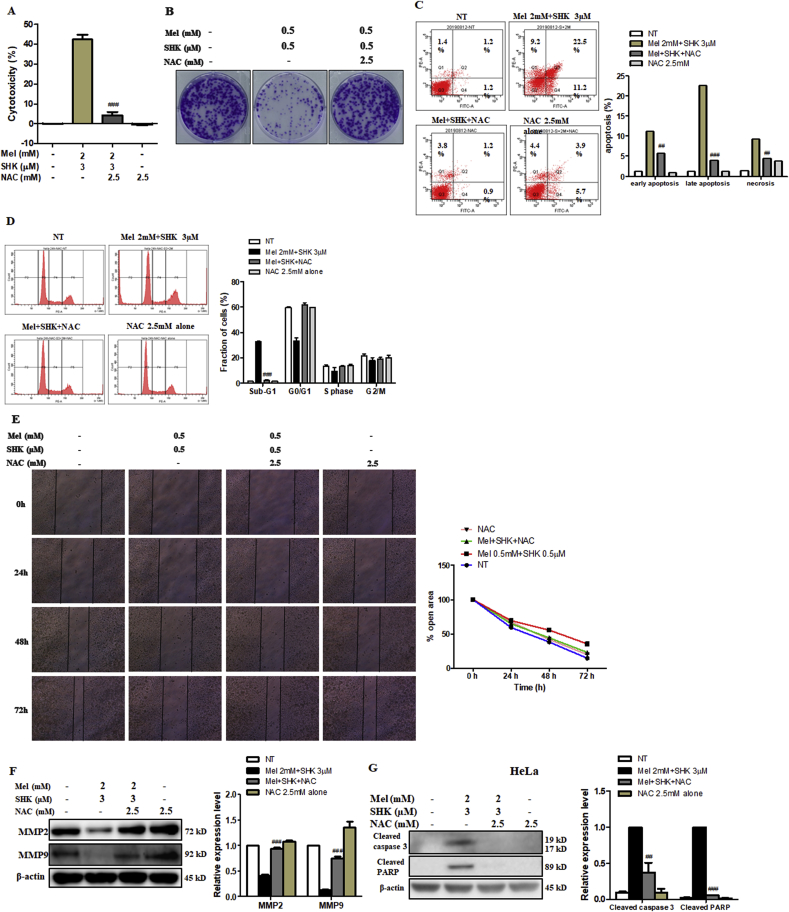
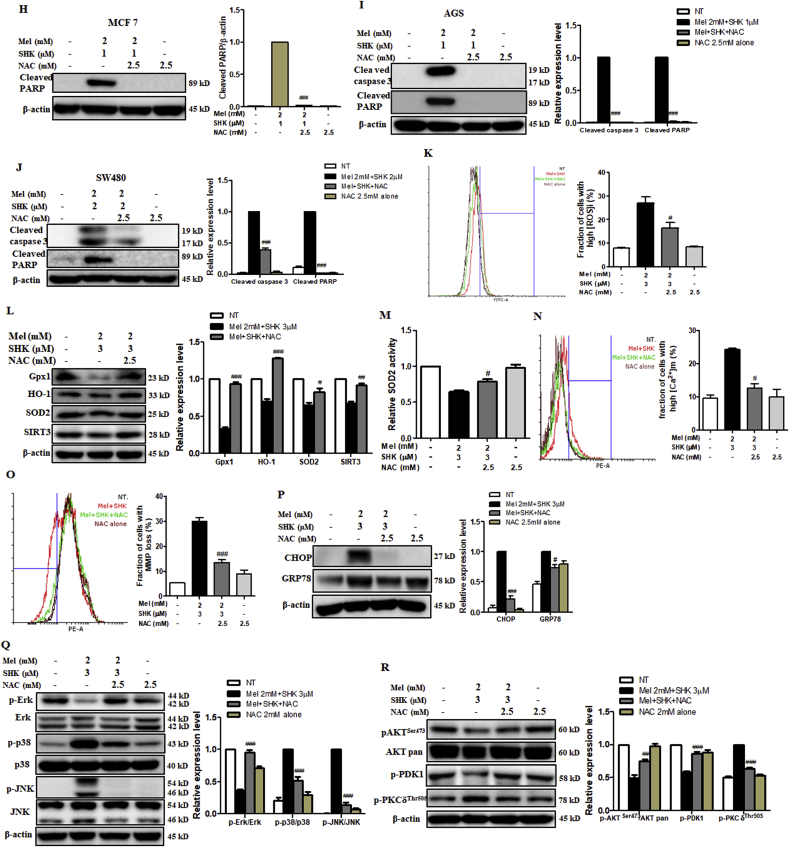
Fig. 7.
Effects of the reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenger, NAC, on the anti-cancer effects of melatonin-shikonin (Mel-SHK) in HeLa, MCF7, AGS, and SW480 cells. HeLa cells were pre-treated with NAC followed by Mel-SHK. The effects on (A) cytotoxicity, (B) clonogenicity, (C) apoptosis [Annexin V/PI double-staining], (D) sub-G1 area, and (E) cell migration were evaluated to confirm the role of ROS. (F) Western blotting was performed to analyse the levels of specific proteins related to cell migration, such as matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP2) and MMP9. The protective effects of NAC against Mel-SHK-induced apoptosis including caspase-3 and/or PARP cleavage, were determined in (G) HeLa, (H) MCF7, (I) AGS and (J) SW480 cells. The ability of NAC to reverse Mel-SHK-mediated (K) ROS generation, (L) oxidative stress-related protein expression, (M) SOD2 activation, (N) mitochondrial calcium (Ca2+) accumulation, (O) MMP losses and (P) ER-stress related protein expression were also investigated. (Q, R) Western blot analysis of the effects of NAC on the expression of MAPK and AKT pathway-related proteins in Mel-SHK-treated cells. The Mel-SHK treatment duration was 24 h for all experiments except those described in B (10 days), K (6 h) and L, M, N, P, Q and R (12 h). Relative protein expression was calculated for all the proteins in western blots. Actin was used for normalisation and as a loading control. Flow cytometry data are presented as histograms and bar graphs. One representative figure from at least three independent experiments is shown for each assay. The data in each bar graph are presented as the means ± SEM. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, and ###P < 0.001 relative to Mel-SHK treated cells.