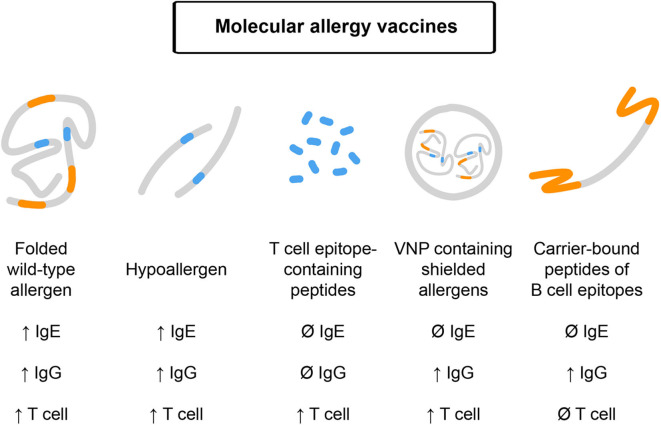
Figure 2.
Molecular allergy vaccines which may be used for prophylactic vaccination and their features. Effects on IgE, IgG, and T cell responses upon administration are indicated. From left to right: Folded, wildtype-like recombinant allergens contain allergen-specific IgE, IgG, and T cell epitopes and may boost these responses upon immunization. Recombinant hypoallergens show reduced IgE reactivity but upon vaccination may induce allergen-specific IgE, IgG, and T cell responses. T cell epitope-containing peptides lack IgE and IgG reactivity and accordingly target T cells without inducing IgE or IgG responses. Virus-like nanoparticles can be produced to contain shielded allergens lacking IgE reactivity but may induce IgG and T cell responses. B cell epitope-based peptide carrier vaccines lack allergen-specific IgE and T cell reactivity and induce allergen-specific IgG responses without boosting allergen-specific IgE and T cell responses.