Figure 1.
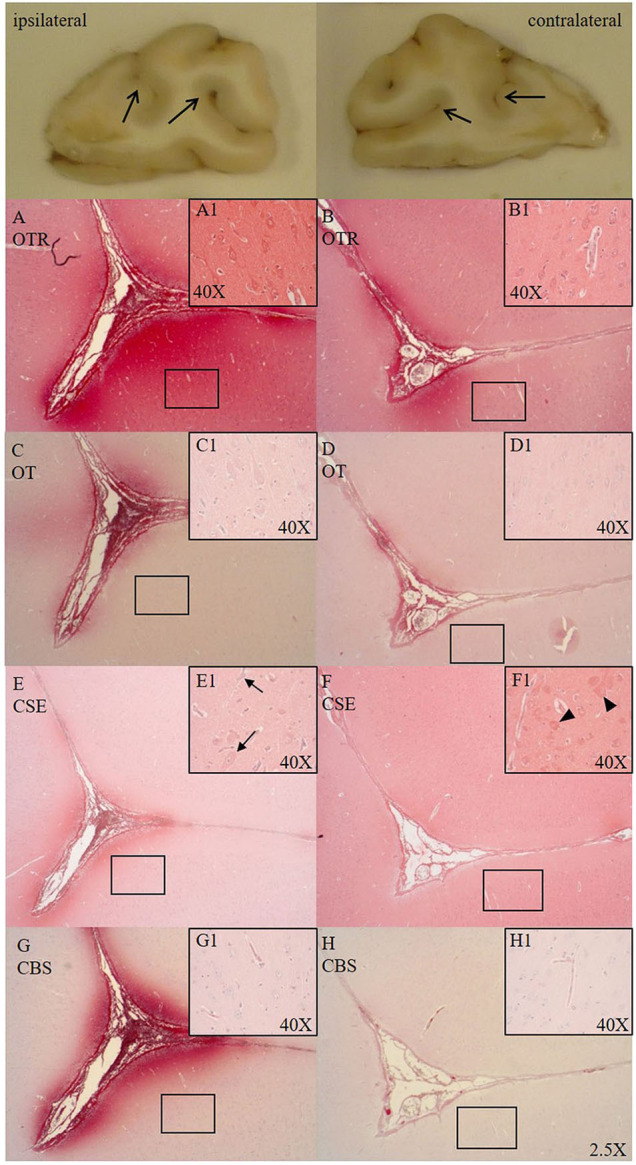
Comparison of OTR (A,B, n = 6), OT (C,D, n = 7), CSE (E,F, n = 7), and CBS (G,H, n = 6) expression in matching consecutive sections of a sulcus of the frontal cortex [ipsilateral (A,C,E,G) vs. contralateral side (B,D,F,H)]. Macroscopic exemplary sections are shown at the top (open arrows pointing to sulci). Ipsilateral OTR expression in the pial vasculature and glia limitans with blushing effect in the parenchyma surrounding the base of the sulcus (A), cortical neurons magnified in (A1), less pronounced OTR expression on the contralateral site (B), cortical neurons magnified in (B1). OT expression is more limited than OTR expression but shows the same expression pattern as OTR in the ipsi- (C, magnified in C1) and contralateral side (D, magnified in D1). In the ipsilateral side CSE is pronouncedly expressed surrounding the sulcus and negative in the parenchyma moving away from the sulcus (E) and shows little to no expression in cortical neurons, with nuclear counter-staining with hematoxylin (black arrows magnified in E1). CSE is expressed in the pial vasculature and is evenly distributed in parenchyma of the contralateral side around the sulcus (F) with (red) CSE-positive cortical neurons (black arrow heads magnified in F1). In the ipsilateral side CBS shows pronounced expression surrounding the sulcus (G) and is not expressed in cortical neurons (magnified in G1). CBS expression in the contralateral side is weak (H) and present in the microvasculature (magnified in H1). OTR: oxytocin receptor; OT, oxytocin; CSE, cystathionine-ɤ-lyase; CBS, cystathionine-β-synthase.
