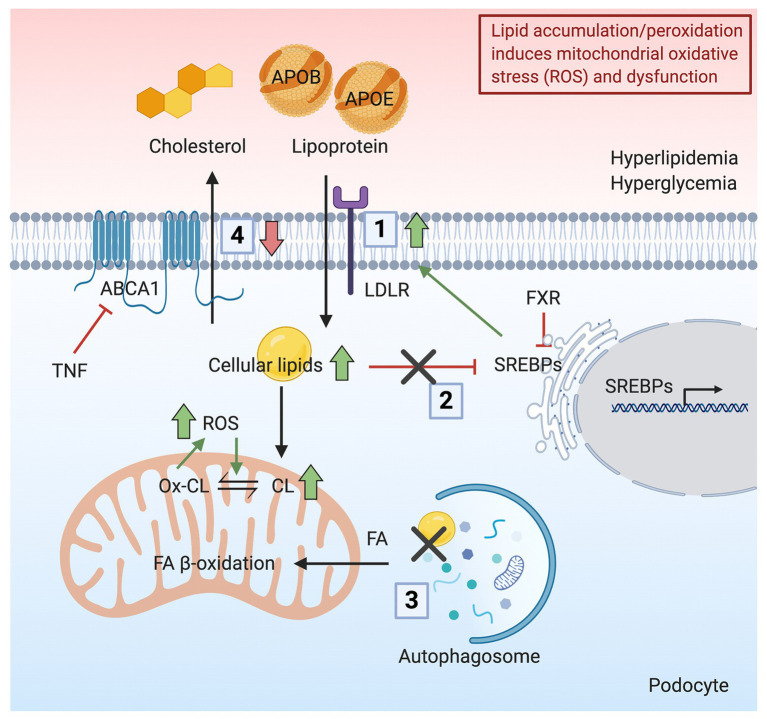
Figure 2.
Schematic representation indicating how lipid accumulation/peroxidation induces mitochondrial oxidative stress and dysfunction. Podocyte lipid accumulation and increased peroxidation induces ROS production and mitochondrial dysfunction. (1) In the presence of hyperlipidemia, increased uptake of apolipoprotein B (APOB)‐ and apolipoprotein E (APOE)-rich lipoproteins occurs in podocytes through the LDLR, resulting in a lipid-rich environment. (2) Hyperglycemia disrupts the feedback regulation of sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs), causing further lipid accumulation. (3) Cellular lipids, mainly in the form of triglycerides, stored in lipid droplets (LDs) are hydrolyzed and delivered as FAs to mitochondria by autophagic clearance. The inhibition of autophagic clearance of lipids is associated with increased lipid endocytosis. (4) Downregulation of ABCA1 impairs reverse cholesterol transport, resulting in the accumulation of cholesterol and CL and peroxidation of CL. Together, the accumulation of lipids in podocytes induces ROS production and mitochondrial dysfunction.