Figure 3.
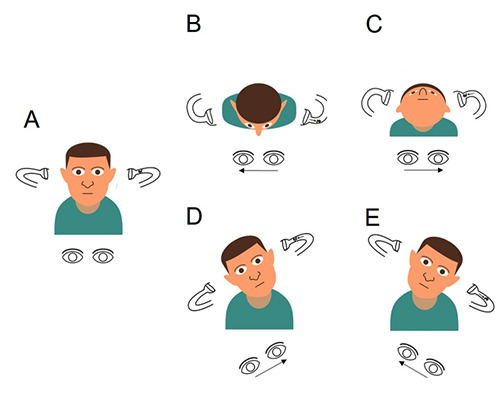
Schematic representation of diagnostic tests in upright position by taking as an example the clinical case of patient n.11 presenting with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) involving the ampullary arm of the left lateral semicircular canal (LSC) (left apogeotropic LSC-BPPV). Arrows within the canal represent the direction of endolymphatic flows, whereas arrows beneath the eyes represent the direction of the fast phase of nystagmus. A) Pseudo Spontaneous Nystagmus: absent. B) Head Pitch Test (HPT) with forward head bending eliciting right-beating nystagmus due to debris moving away from left LSC ampulla. C) HPT with backward head bending evoking ampullifugal endolymphatic flows, thus resulting in left-beating nystagmus. D) Upright Head Roll Test (UHRT) with rightward head tilting eliciting left-beating apogeotropic nystagmus as particles floats toward left LSC ampulla. E) UHRT with leftward head tilting generating right-beating apogeotropic nystagmus due to otoliths shifting away from left LSC ampulla.
