Figure 4.
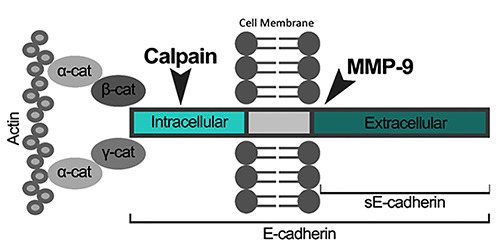
Schematic representation of an E-cadherin molecule and it’s proteolysis by two different enzymes. In the intracellular end, the molecule is connected to a cell’s cytoskeleton component – actin -, using catenin (cat) as a mediator. In the same intracellular end, E-cadherin is susceptible to Calpain’s action. In the extracellular domain, the cleavage of E-cadherin by MMP-9 creates an extracellular fragment of 80 KDa, also known as soluble E-cadherin (sE-Cadherin).
