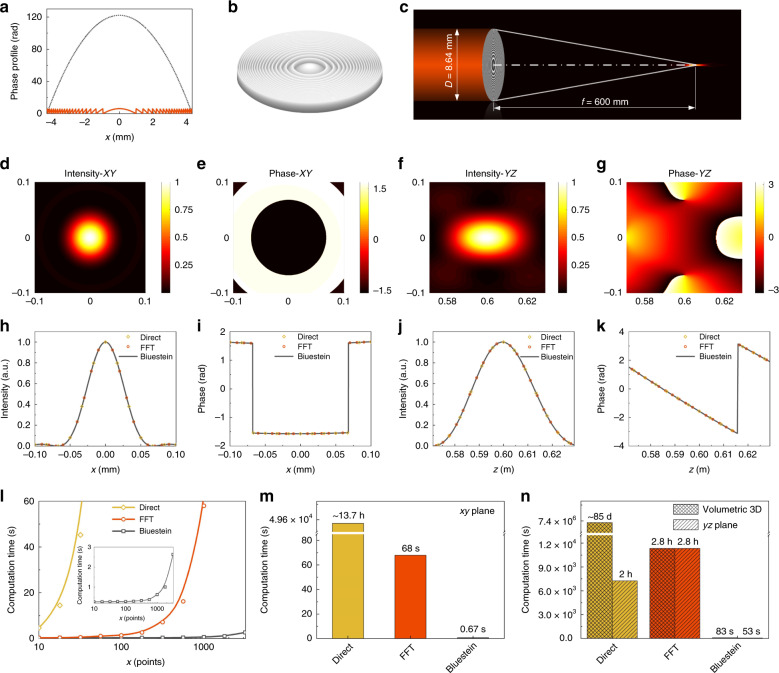
Fig. 2. Scalar calculation of the converging spherical wave.
a Phase profiles of the convex lens (gray line) and the corresponding phase plate (red line). b 3D rendered diagram of the phase plate. c Illustration of the optical setup. d Intensity and e phase distributions in the focal plane (z = 600 mm). f Intensity and g phase distributions in the longitudinal direction. h–k Line plots corresponding to (d–g), calculated using three different methods. l Dependence of the computation time on the number of sampling points in one dimension. An incident light field with sampling points of 1080 × 1080 and an interval of 8 μm (i.e., width of 8.64 mm) is fixed for each calculation (the same hereinafter unless otherwise specified). m Comparison of the computation time for the light field in the xy-plane using different methods. Here, the target region with a width of 0.2 mm is fixed with sampling points of 1080 × 1080. n Comparison of the computation time for the light field in volumetric three dimensions and the cross-sectional yz-plane using different methods. Here, 150 sliced layers are calculated