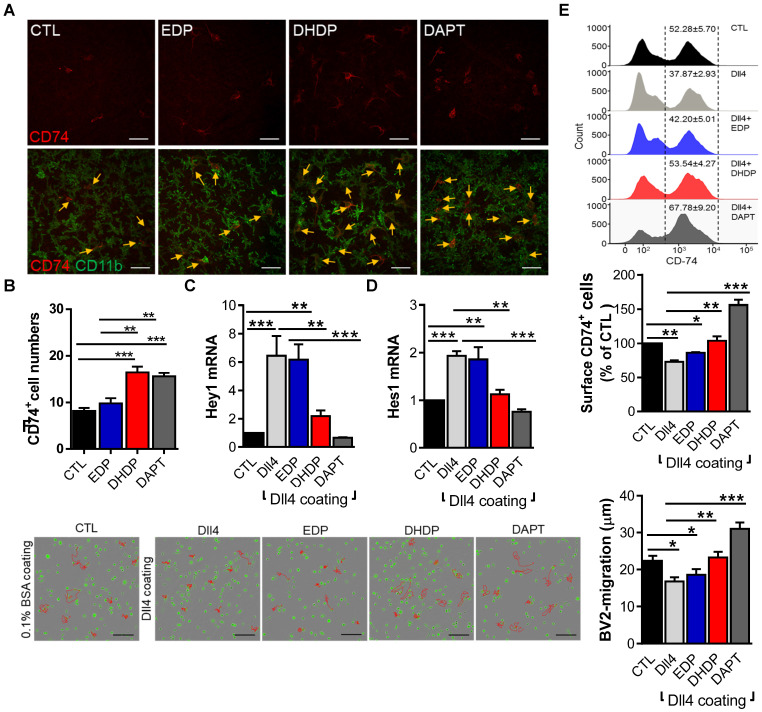
Figure 5.
19,20-EDP and 19,20-DHDP impact Notch signaling and microglial activation. (A-B) For ex vivo retinal explants cultures, retinae from one-month old PKD rats were incubated for 24 hours in 10 µmol/L sEH-I with 0.03% DMSO (CTL), 3 µmol/L EDP, 3 µmol/L DHDP or 10 µmol/L DAPT. (A) CD74+ (red) and CD11b+ (green) retinal microglia, the yellow arrows indicate CD74+ microglia; bar = 50 µm. (B) Quantification of CD74+ microglial cells; n = 4, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA with Turkey's multiple comparison test). (C-F) BV-2 cells were seeded on plates coated with 0.1% BSA (CTL) or Dll4 (500 ng/mL) in the continued presence of sEH-I (10 µmol/L) and treated for 24 hours with 19,20-EDP (3 μmol/L), 19,20-DHDP (3 μmol/L) or γ-secretase inhibitor (DAPT,10 μmol/L). (C-D) RT-qPCR analysis of Hey1 (C) and Hes1 (D) mRNA in retinal explants. (E) Surface expression of CD74 on BV-2 microglial cells. (F) Mobility tracing of microglia (red lines) over a period of 4 hours. The average mobility was calculated as μm/frame (15 minutes intervals); bar = 200 µm. (C-F) n = 4, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison test).