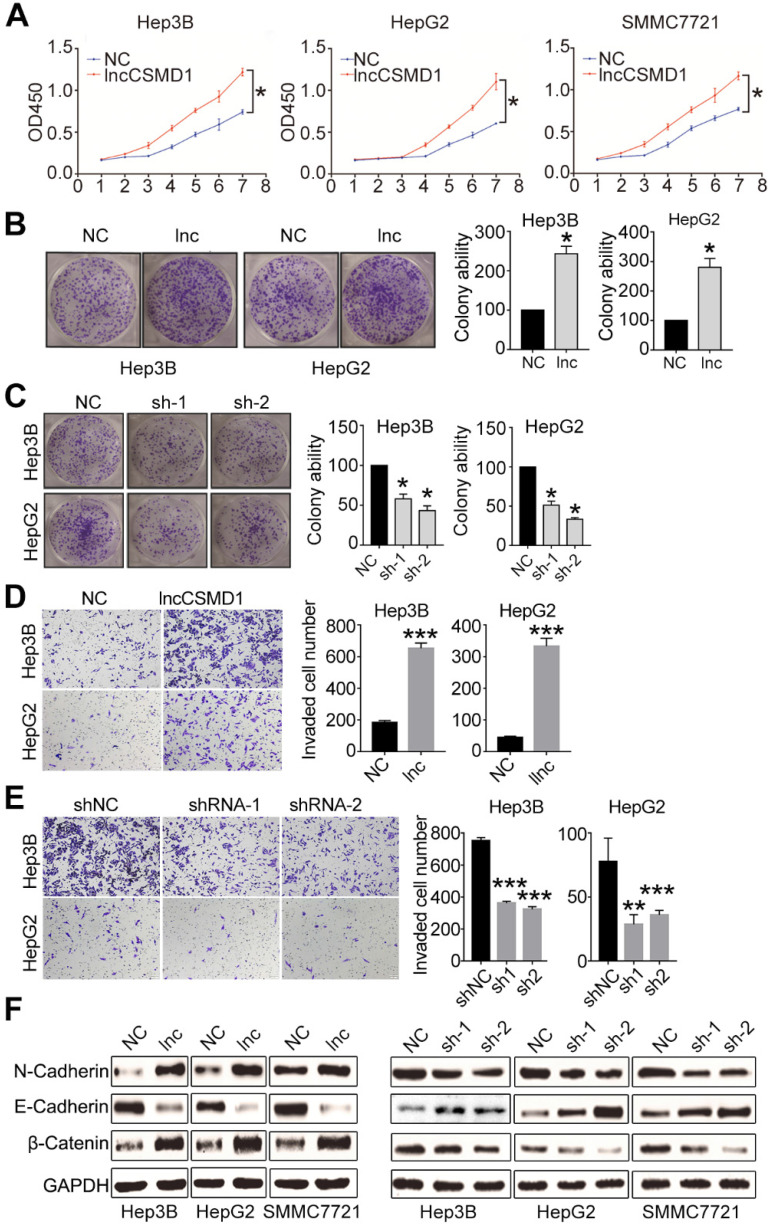
Figure 2.
Ectopic expression of lncCSMD1 promotes proliferation, colony formation and invasion of HCC cells in vitro. (A) The ectopic expression of lncCSMD1 markedly promotes cell proliferation in Hep3B, HepG2 and SMMC7721 HCC cells, which were determined by CCK-8 assay. (B) lncCSMD1 overexpression significantly enhances colony formation in Hep3B and HepG2 HCC cells compared with the control cells. Data represent the mean ± SD of triplicate experiments and was analyzed by Student t test. * means p <0.05. (also applies to the following). (C) Downregulated lncCSMD1 notably inhibits colony formation in Hep3B and HepG2 HCC cells compared with the control cells. (D) In transwell assay, lncCSMD1 expression strikingly raises the cell invasion in Hep3B and HepG2 cells compared with the control cells. (E) In transwell assay, downregulated lncCSMD1 by shRNA markedly reduces the cell invasion in Hep3B and HepG2 cells compared with the control cells. (F) Overexpression of lncCSMD1 causes the expression of mesenchymal proteins (N-cadherin and β-catenin) and reduces the expression of epithelial protein (E-cadherin) in Hep3B, HepG2 and SMMC7721 cells, as shown by western blot.