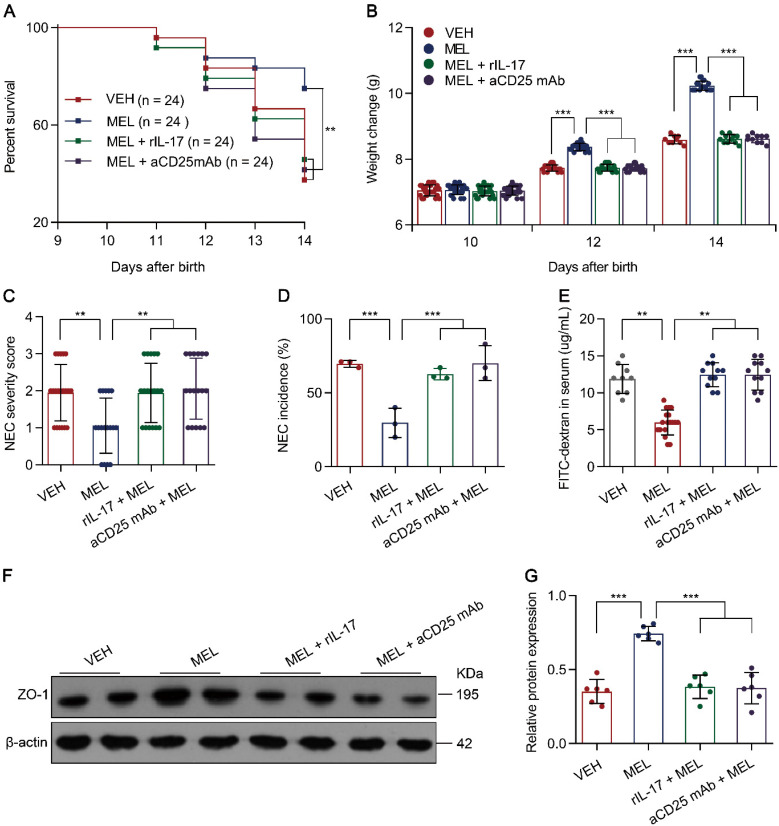
Figure 3.
Melatonin effects require Th17/Treg balance. (A) Kaplan-Meier estimates and log-rank tests were used to analyze the survival rates of pups following necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) induction upon treatment with only vehicle (VEH) or with melatonin (MEL), melatonin combined with rIL-17 (MEL + rIL-17), or melatonin combined with aCD25mAb (MEL + aCD25mAb). **P < 0.01. (B) Weight change of mouse pups in VEH, MEL, MEL + rIL-17, and MEL + aCD25mAb groups. (C) NEC severity scores of the histopathological evaluation of mouse ilea (n = 20 for VEH, 17 for MEL, 18 for MEL + rIL-17, and 17 for MEL + aCD25mAb groups). (D) Incidence of NEC (damage scores > 2) in VEH, MEL, MEL + rIL-17, and MEL + aCD25mAb groups. (E) Fluorescence readings in plasma 4 h after gavage with FITC-dextran from VEH (n = 9), MEL (n = 18), MEL + rIL-17 (n = 11) and MEL + aCD25mAb (n = 11) groups. (F) Immunoblot analysis of the expression of ZO-1 in ilea of VEH, MEL, MEL + rIL-17 and MEL + aCD25mAb group pups. (G) Quantification of (F) (n = 6). Each symbol (B, C, E, G) represents an individual mouse and (D) shows the incidence of each independent experiment (n = 24); column graphs represent the mean with error bars indicating standard deviation (SD), **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. P values were derived through one-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni multiple comparison test (B-E, G). Data are representative of three independent experiments (A-E, G).