Fig. 1. Landscape of RNA m6A methylation in C.elegans.
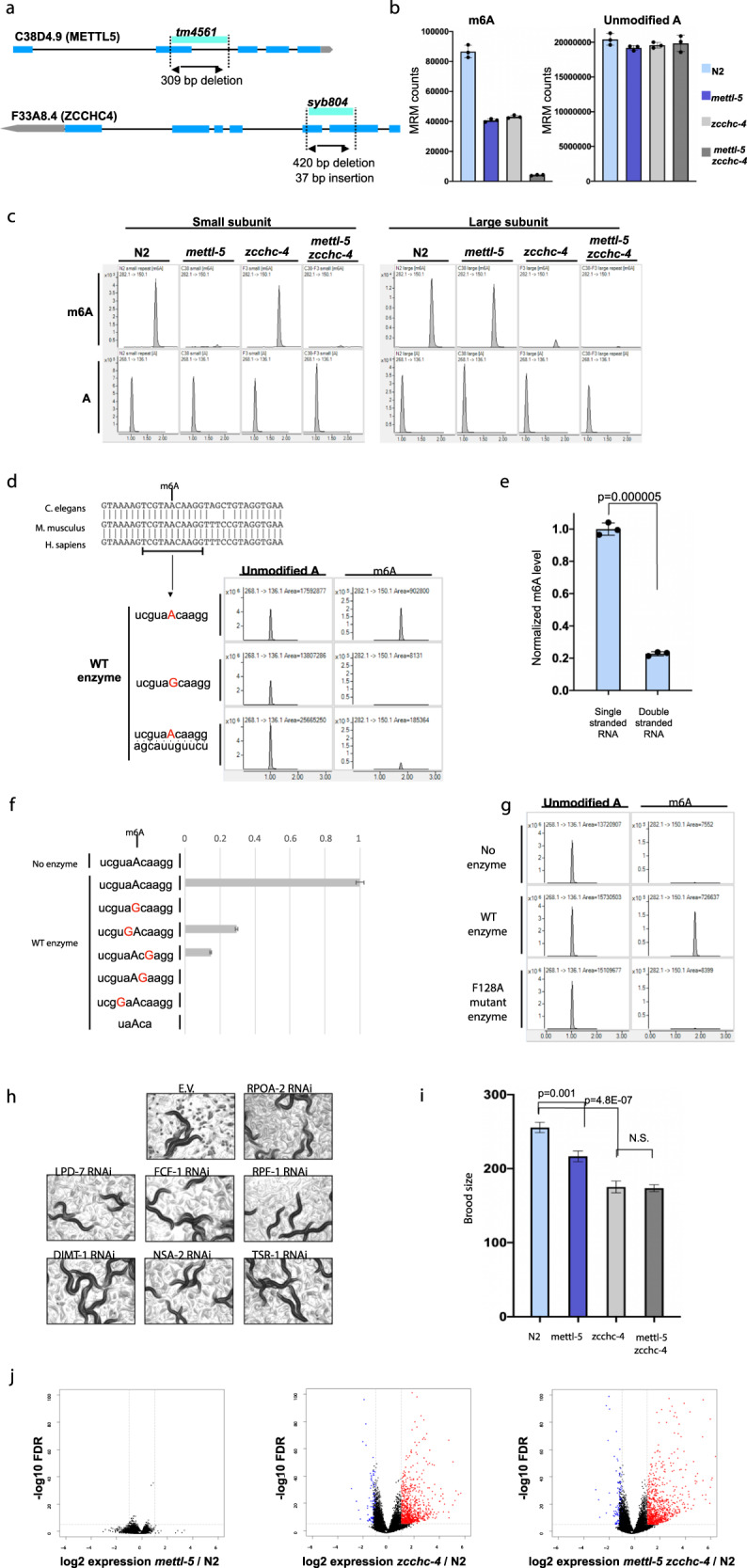
a Diagrams depicting the mettl-5 and zcchc-4 mutants used in this study. b HPLC–MS/MS measurement of m6A and unmodified A MRM counts of total RNA from indicated worm strains. The experiments were performed in biological triplicates and error bars represent standard deviation. c HPLC–MS/MS peaks of small and large subunit ribosomal RNA isolated from indicated worm strains. d Worm, mouse, and human rRNA sequence alignment encompassing 11 bp RNA oligo sequence used in in vitro methylation reactions. HPLC–MS/MS peaks of in vitro methyltransferase reactions employing recombinant wild-type worm METTL5 protein and single or double-stranded RNA oligos with indicated sequences. e Quantification of HPLC–MS/MS analysis of in vitro methylation reactions using single stranded or double stranded 11 bp RNA oligos that are shown in d. Error bars represent standard deviation. f Quantification of HPLC–MS/MS analysis of in vitro methylation reactions employing recombinant worm METTL5 and RNA oligos with the indicated sequences, which demonstrates the substrate sequence and length specificity of METTL5 enzyme. g HPLC–MS/MS peaks of in vitro methylation reactions employing 11 bp rRNA oligo using wild-type or catalytically inactive F128A mutant recombinant METTL5 enzyme. h Images of worm plates showing adults and worm embryos indicating decrease in fertility after RNAi-mediated knock down of indicated rRNA biogenesis genes—rpoa-2 (F14B4.3), lpd-7 (R13A5.12), fcf-1 (F30A10.9), rpf-1 (F44G4.1), dimt-1 (E02H1.1), nsa-2 (W09C5.1), tsr-1 (F10G7.1) and E.V. (empty vector). i Bar graph depicting the brood size of indicated worm strains at 20 °C. Error bars represent standard error. j Volcano plots depicting statistically significant gene expression changes of embryos of indicated strains. Red depicts upregulated transcripts whereas blue downregulated transcripts.
