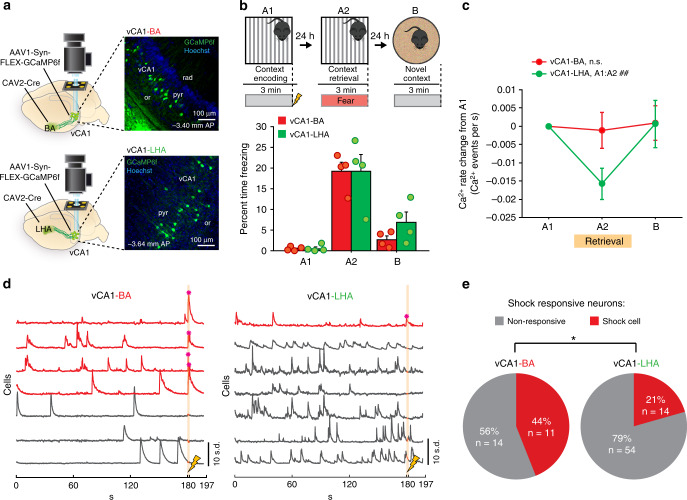
Fig. 1. The vCA1-BA projection is enriched in shock responsive neurons.
a Experimental design for vCA1 projection-specific Ca2+ imaging. Cre-dependent GCaMP6f was virally expressed in vCA1 and CAV2-Cre injected in either the BA (top) or LHA (bottom) in order to selectively express GCaMP6f in vCA1-BA or vCA1-LHA projecting neurons. The main effects of this experiment were consistent across all mice within each group. b vCA1-BA and vCA1-LHA mice exhibited similar freezing across contextual fear conditioning Ca2+ imaging days (repeated-measures ANOVA; % freezing*group interaction, F(1,6) = 0.46, p = 0.48, NBA = 4, NLHA = 4). c The vCA1-LHA (but not vCA1-BA) projection has a significant decrease in Ca2+ event rate during A2 retrieval (BA Ncells = 25, LHA Ncells = 68|Mann–Whitney between groups with Bonferroni alpha correction; A2–A1 U = 681.00, p = 0.14, B–A1 U = 798.50, p = 0.66|Friedman across 3 days (within-group) with post-hoc wilcoxon sign rank A1:A2 and B:A1 (with Bonferroni alpha correction); BA: Friedman X2(2) = 2.06, p = 0.36, A1:A2 Z = −1.26, p = 0.36; LHA: Friedman X2(2) = 9.93, p = 0.0070, A1:A2 Z = −3.34, ##p = 0.0008, B:A1 Z = −0.45, p = 0.65). d Example Ca2+ traces from a vCA1-BA (left) and vCA1-LHA (right) FOV during A1 context encoding showing shock responsive neurons in red and Ca2+ transients during the shock marked with an asterisk. e The vCA1-BA projection has significantly more shock cells than the vCA1-LHA projection (Chi-squared test of proportions X2(1) = 5.10, *p = 0.0240, NBA = 25, NLHA = 68). Error bars, ±s.e.m. Statistical tests comparing distributions were two-sided. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.