Figure 4. Activation of wild-type GCase by S-181 lowers oxidized dopamine and α-synuclein in non-GBA1-linked PD patient iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons.
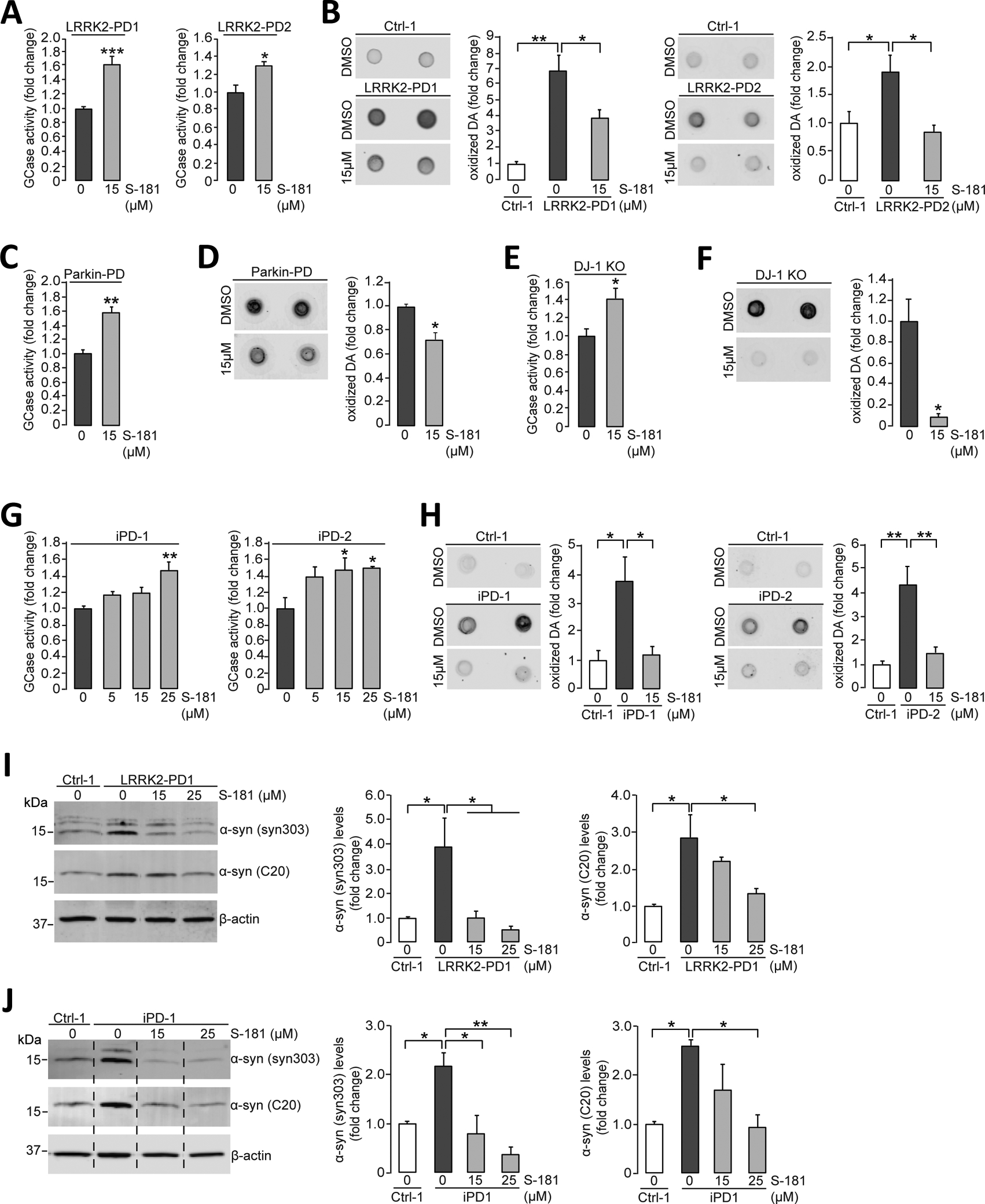
(A) Mutant iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons carrying the LRRK2 R1441C mutation (LRRK2-PD1) or G2019S mutation (LRRK2-PD2) were treated with either DMSO (vehicle) or S-181 (15μM) for 10 days. Cell lysates were then analyzed at day 100 of differentiation for GCase activity assessed by in vitro enzyme activity assay (N=6 to 9 independent experiments for LRRK2-PD1; N=3 independent experiments for LRRK2-PD2). (B) Mutant iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons (LRRK2-PD1 and LRRK2-PD2) and healthy control iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons were treated with either DMSO (vehicle) or S-181 (15μM) for 10 days. Cell lysates were analyzed at day 100 of differentiation for oxidized dopamine (DA) by near-infrared fluorescence assay (N=7 independent experiments for LRRK2-PD1; N= 4–5 independent experiments for LRRK2-PD2). (C and D) Mutant iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons generated from fibroblasts of a patient with a compound heterozygous PARKIN mutation were treated with either DMSO (vehicle) or S-181 (15μM) for 10 days. Cell lysates were analyzed at day 150 of differentiation for (C) GCase activity assessed by in vitro enzyme activity assay (N=3 independent experiments) and (D) oxidized DA measured by near-infrared fluorescence assay (N=3 independent experiments). (E and F) Mutant iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons in which DJ-1 was deleted by CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing (DJ-1 KO) were treated with either DMSO (vehicle) or S-181 (15μM) for 10 days. Cell lysates were analyzed at day 160 of differentiation for (E) GCase activity by in vitro enzyme activity assay (N=3 independent experiments) and (F) oxidized DA measured by near-infrared fluorescence assay (N=3 independent experiments). (G) iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons generated from fibroblasts from two patients with idiopathic PD (iPD-1 and iPD-2) were treated with either DMSO (vehicle) or S-181 (5, 15, and 25μM) for 10 days. Cell lysates were analyzed at day 130 of differentiation for GCase activity (N=4 to 5 independent experiments for iPD1; N=3 to 5 independent experiments for iPD2). (H) iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons generated from fibroblasts from two patients with idiopathic PD (iPD-1 and iPD-2) and one healthy control (Ctrl-1) were treated with either DMSO (vehicle) or S-181 (15μM) for 10 days. Cell lysates were analyzed at day 130 of differentiation for oxidized DA measured by near-infrared fluorescence assay (N=3 to 4 independent experiments for iPD1; N= 3 to 6 independent experiments for iPD2). (I) Mutant iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons carrying the LRRK2 G2019S mutation (LRRK2-PD1) and healthy control iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons (Ctrl-1) were treated with either DMSO (vehicle) or S-181 (15 and 25μM) for 10 days. Triton-soluble lysates were analyzed at day 100 of differentiation for the amount of α-synuclein by immunoblotting with C20 and syn303 anti-α-synuclein antibodies. β-Actin was used as a loading control (N=3 to 4 independent experiments). (J) iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons generated from fibroblasts from a patient with idiopathic PD (iPD-1) and a healthy control (Ctrl-1) were treated with either DMSO (vehicle) or S-181 (15 and 25μM) for 10 days. Triton-soluble lysates were analyzed at day 100 of differentiation for the amount of α-synuclein by immunoblotting with C20 and syn303 anti-α-synuclein antibodies. β-Actin was used as a loading control (N=3 to 4 independent experiments). Error bars, mean ± SEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001, Student’s t test (A and C to F) or one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test (B and G to J).
