Figure 5. Activation of wild-type GCase by S-181 reduces lipid substrates and α-synuclein in mice.
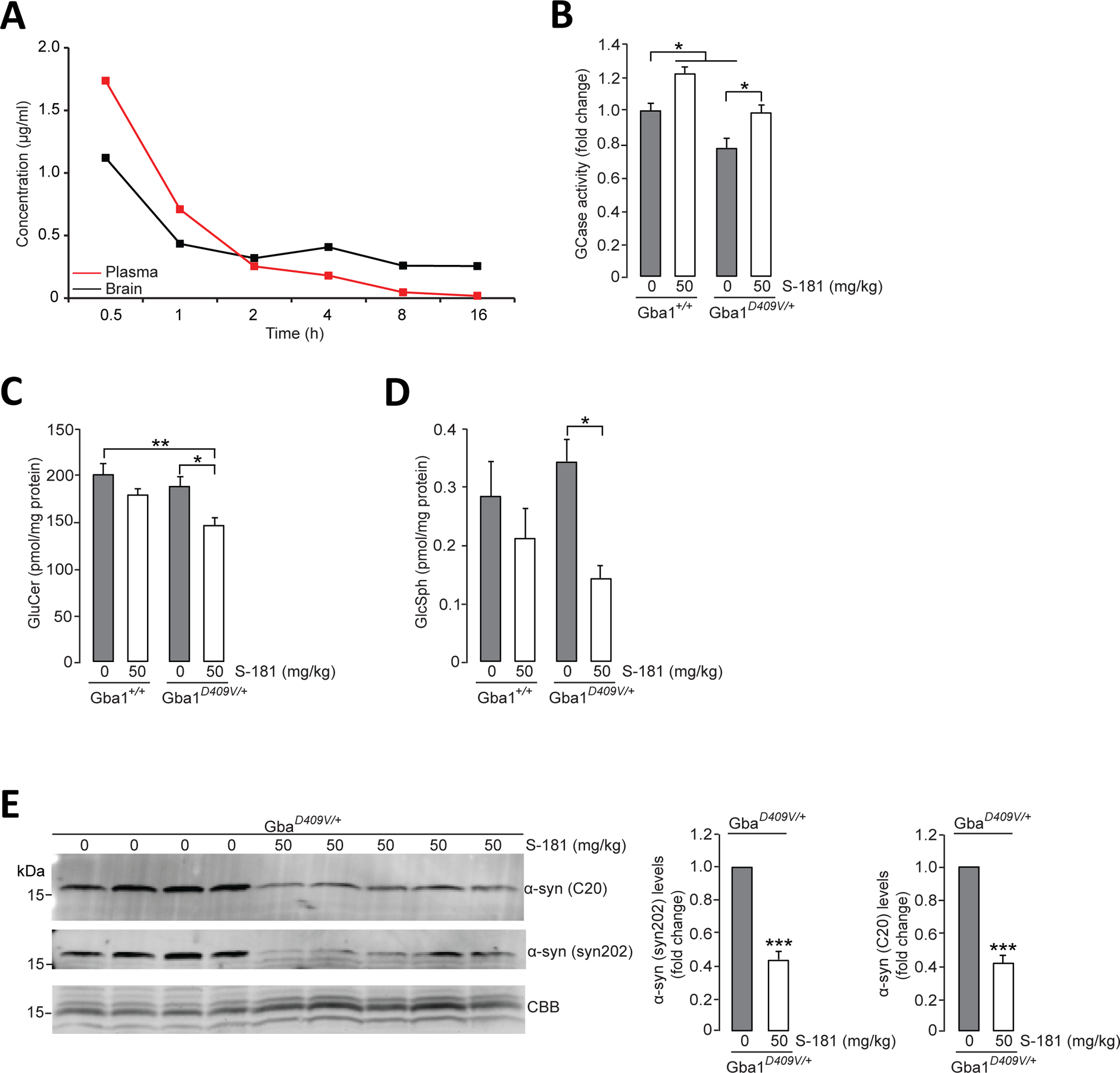
(A) Mean concentration-time profiles for S-181 in plasma and brain tissue after administration of intraperitoneal single dose (50 mg/kg) to C57BL/6 wild-type mice (n=3 mice per time point). (B) GCase activity was measured by in vitro enzyme activity assay in lysates of hippocampal tissue from wild-type Gba1+/+ mice and from Gba1D409V/+ heterozygous mutant mice that had been treated with 5% dextrose (vehicle) (n=8 mice per group) or S-181 (50mg/kg; n=5 mice per group) intraperitoneally twice daily for 15 days. (C and D) Quantification of intracellular (C) glucosylceramide (GluCer) and (D) glucosylsphingosine (GluSph) by mass spectrometry in hippocampal tissue from wild-type Gba1+/+ and Gba1D409V/+ heterozygous mutant mice treated with 5% dextrose (vehicle) (n=8 mice per group) or S-181 (50mg/kg; n=5 to 6 mice per group) intraperitoneally twice daily for 15 days. (E) Immunoblot analysis of α-synuclein (using C20 and syn202 anti-α-synuclein antibodies) in Triton-insoluble lysates of hippocampal tissue from Gba1D409V/+ heterozygous mutant mice treated with 5% dextrose (vehicle) (n=8 mice per group) or S-181 (50mg/kg; n=5 mice per group) intraperitoneally twice daily for 15 days. Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) was used as a loading control. Mice (mixed group of males and females) were between 13 and 15 months of age. Error bars, mean ± SEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001, Student’s t test (E) or one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test (B to D).
