Figure 3.
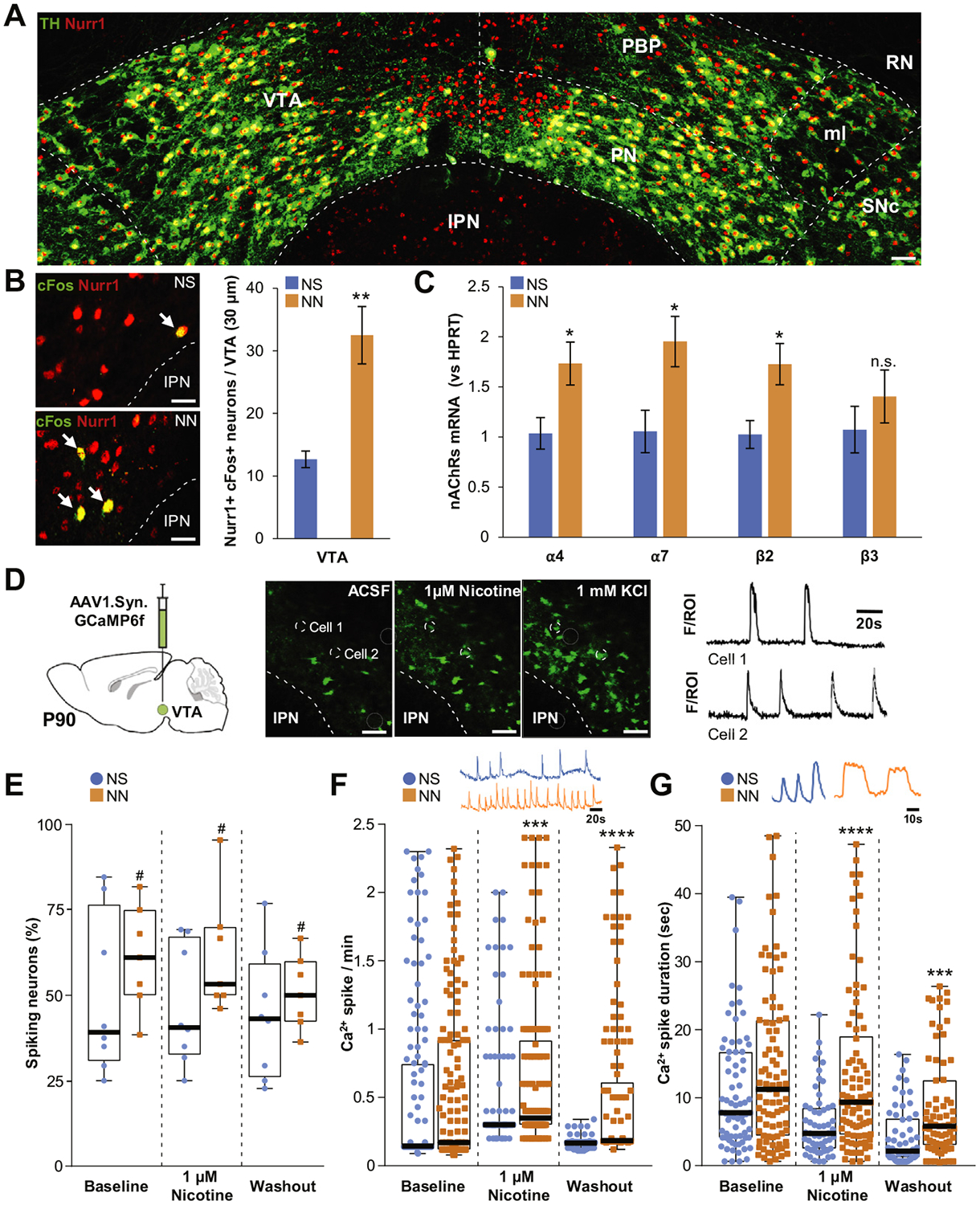
Neonatal nicotine (NN) exposure alters activity of adult ventral tegmental area (VTA) neurons. (A) Representative image of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)/Nurr1 immunoreactivity in the VTA of adult mouse (postnatal day 90 [P90]). Scale bar = 60 μm. (B) Nurr1 and cFos epifluorescence immunoreactivity staining (left panels) in neonatal saline (NS)- exposed (top) and NN-exposed (bottom) mouse VTA. NN increases cFos immunoreactivity (arrows) in Nurr11 VTA neurons (graph, n = 6 mice per group, t10 = 3.59, p, .01). Graph shows mean ± SE. **p, .01. (C) NN exposure upregulates the messenger RNAs (mRNAs) of specific nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) subunits in the VTA. Quantification shows a significant relative increase of a4 (t10 = 2.7, p, .05), a7 (t10 = 2.74, p, .05), and b2 transcripts (t10 = 2.94, p, .05) in NN-exposed mice (n = 6 mice per group). Graph shows mean 6 SE. *p, .05. (D) Calcium indicator GCaMP6f was expressed in VTA neurons via adeno-associated virus (AAV) injections (left). Ca21 activity (middle panels) was recorded during artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF), 1 mM nicotine, or 1 mM KCl perfusion. Changes in fluorescence (F) were analyzed for individual neurons (region of interest [ROI]) to generate calcium spike traces (cell 1, cell 2, right). Dashed circles show two representative VTA neurons responding to 1 mM nicotine perfusion. Scale bar = 100 mm. (E) NN-treated mice display an overall increase of active (spiking) neurons (%) (F1,39 = 4.35, p, .05). #Main effect: pNN, .05. (F) NN-treated mice display enhanced Ca2+spike frequency during nicotine perfusion (U = 6364, p, .001, Mann-Whitney U test) that persists during washout (U = 1185, p, .0001, Mann-Whitney U test). (G) NN exposure increases average Ca21 spike duration during (U = 1462, p, .0001, Mann-Whitney U test) and after (U = 1257, p, .001, Mann-Whitney U test) nicotine perfusion. Graphs (E–G) show all data points with medians and interquartile ranges. ***p, .001, ****p, .0001. Additional statistics are presented in Supplemental Table S1. IPN, interpeduncular nucleus; ml, medial lemniscus; n.s., not significant; PBP, parabrachial pigmented area; PN, paranigral nucleus; RN, red nucleus; SNc, substantia nigra compacta.
