Figure 4.
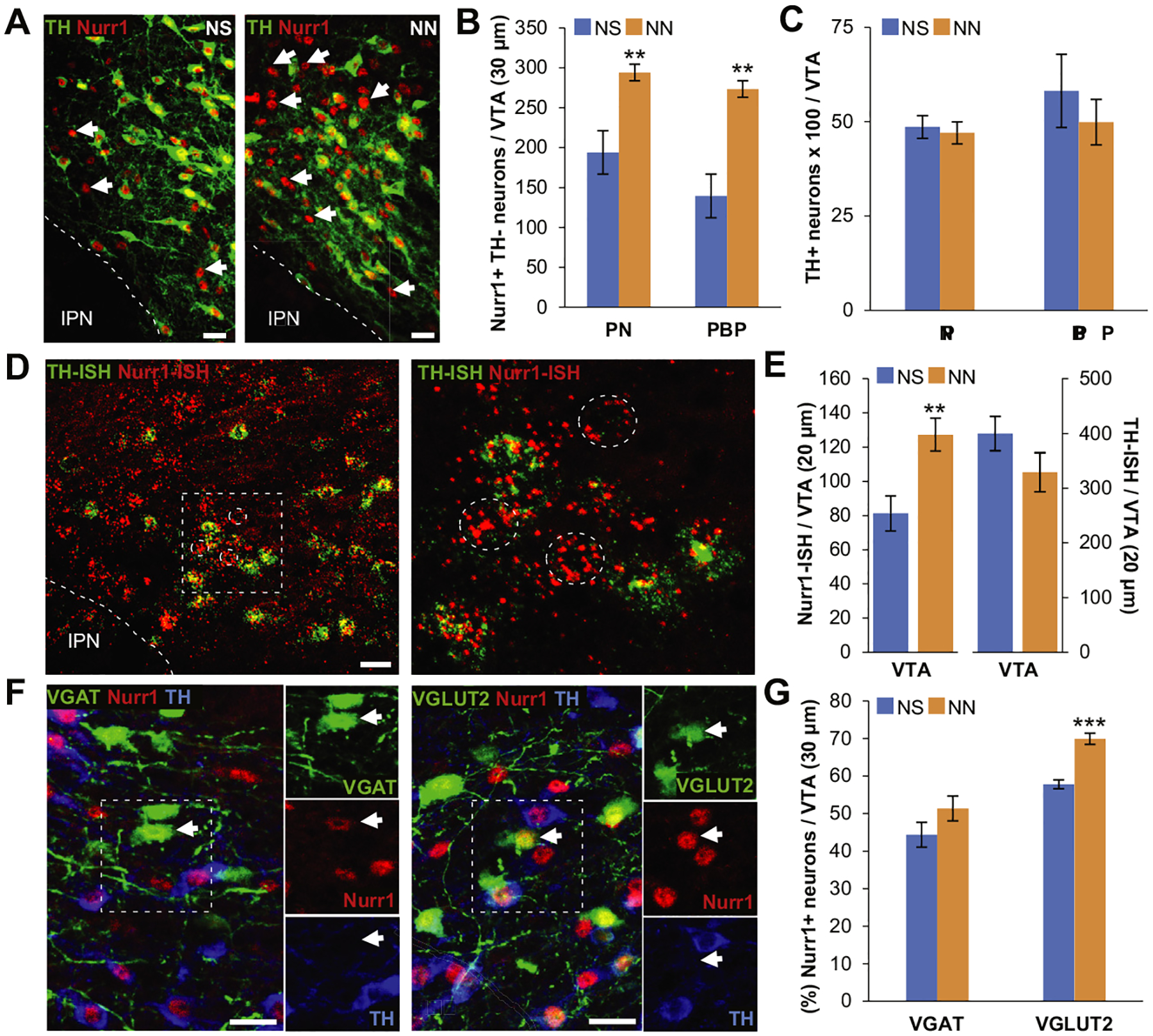
Neonatal nicotine (NN) exposure increases Nurr1 expression in nondopaminergic ventral tegmental area (VTA) neurons. (A) Nurr1 and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) immmunoreactivity of the VTA in neonatal saline (NS)-treated (left) and NN-treated (right) adult (postnatal day 90) mice. Arrows indicate Nurr11 TH2 neurons. Scale bars = 50 mm. (B, C) Epifluorescence quantification indicates that NN exposure increases the number of Nurr11 neurons in both paranigral nucleus (PN) (n = 6 mice per group, t10 = 4.41, p, .001) and parabrachial pigmented area (PBP) (n = 6 mice per group, t10 = 4.37, p, .01) subnuclei of the VTA (B), without affecting the total number of TH1 neurons (C). Graph shows mean ± SE. **p, .01. (D) Nurr1/TH in situ hybridization (ISH) in the VTA of NN-treated adult (postnatal day 90) mice (left). Inset is shown at a higher magnification (right) to indicate nondopaminergic (TH-ISH2) Nurr1-ISH1 neurons (dashed circles). Scale bar = 50 mm. (E) Epifluorescence quantification shows that NN exposure induces an increase in the number of Nurr1-ISH1 neurons (n = 8 sections per group, t14 = 23.27, p, .01), while the number of TH-ISH1 neurons remains constant. Graph shows mean 6 SE. *p, .05. (F) Nurr1, TH, and green fluorescent protein immune reactivity in the VTA of NN-treated VGAT-Cre (left) and VGLUT2-Cre (right) mice injected with a Cre-dependent adeno-associated virus–green fluorescent protein reporter. Arrows indicate nondopaminergic (TH2) gamma-aminobutyric acidergic or glutamatergic neurons expressing Nurr1. Scale bars = 50 mm. (G) Epifluorescence quantification (%) of Nurr11 neurons coexpressing VGAT1 or VGLUT21 in the VTA. NN treatment induces a significant increase in the percentage of Nurr1-expressing glutamatergic neurons (n = 6 mice per group, t10 = 25.8, p, .001). Graph shows mean 6 SE. ***p, .001. IPN, interpeduncular nucleus.
