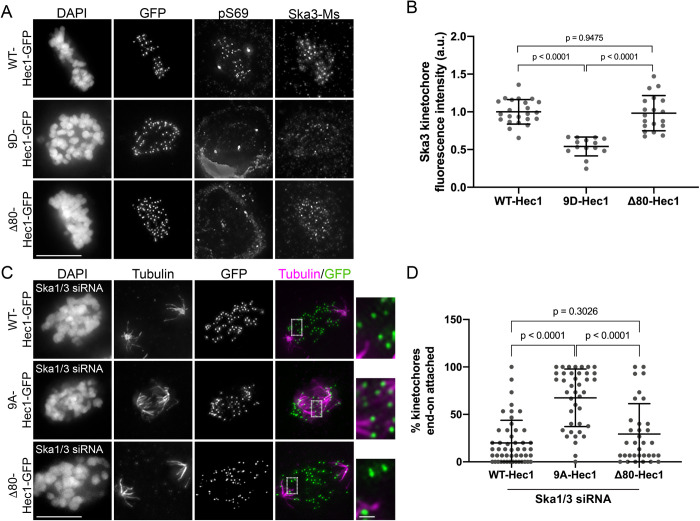
FIGURE 5:
The Hec1 tail domain is dispensable for Ska complex recruitment to kinetochores and is required for kinetochore–microtubule attachments in the absence of the Ska complex. (A) Immunofluorescence images of cells expressing WT, 9D-, and Δ80-Hec1-GFP. Cells were fixed and stained using antibodies to Hec1 pS69 and Ska3 (mouse). (B) Quantification of Ska3 kinetochore fluorescence intensity from cells expressing WT, 9D-, and Δ80-Hec1-GFP. For each condition, at least 20 kinetochores per cell were measured from at least five cells per experiment from three separate experiments. Statistical significance was determined by a one-way ANOVA. (C) Immunofluorescence images of cold-treated cells expressing WT-, 9A-, and Δ80-Hec1-GFP and treated with Ska1 and Ska3 siRNA. Cells were incubated in ice-cold DMEM for 12 min, permeabilized, fixed, and stained with antibodies to tubulin. Insets are enlargements of the regions indicated by the dashed boxes. (D) Quantification of end-on attachment in cells expressing WT-, 9A-, and Δ80-Hec1-GFP and treated with Ska1 and Ska3 siRNA. The WT- and 9A-Hec1 data shown are from the experiment presented in Figure 2. For each condition, at least 15 kinetochores per cell were measured from at least 10 cells per experiment from three separate experiments. Statistical significance was determined by a one-way ANOVA. On all dot plots, each dot represents the average value for all kinetochores from a single cell. Scale bars: 10 and 1 µm for panels and insets, respectively.