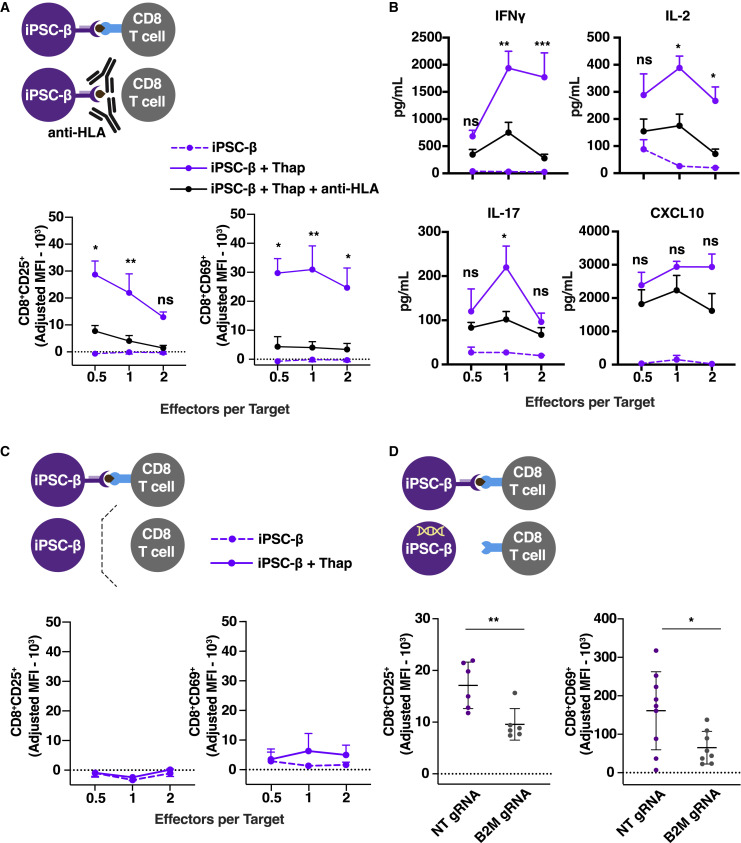
Figure 3.
iPSC-β-Induced T Cell Activation and Killing Is Mediated by Direct T Cell-HLA Interaction
(A and B) PBMCs co-cultured for 48 h with autologous iPSC-β (n = 3 T1D donors, 3 differentiation batches per donor). iPSC-β were pre-treated with thap (5 μM for 5 h) and/or anti-HLA antibody for 30 min before co-culture.
(A) Flow cytometry after 48 h co-culture of T cell activation markers, CD25+ and CD69+, gated on CD8+ cells.
(B) Pro-inflammatory cytokine detection in supernatants collected after 48 h co-culture of PBMCs with autologous iPSC-β ± thap.
(C) Expression of CD25+ and CD69+, gated on CD8+ cells in a transwell system.
(D) Expression of the activation marker CD25+ and CD69+ on CD8+ cells after 48-h co-culture with autologous iPSC-β transduced with a lentivirus vector expressing a non-targeting (NT) or B2M guide RNA (gRNA) and Cas9 (n = 3 T1D donors, n = 3 differentiation batches per donor line). ∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01, Student’s t test. T1D1, T1D2, and T1D3 were pooled together. ns, non-significant.
(A–C) n = 3 T1D donors, n = 3 differentiation batches per donor line. T1D1, T1D2, and T1D3 were pooled together. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.005, and ∗∗∗p < 0.0005; 2-way ANOVA.
See also Figure S3.