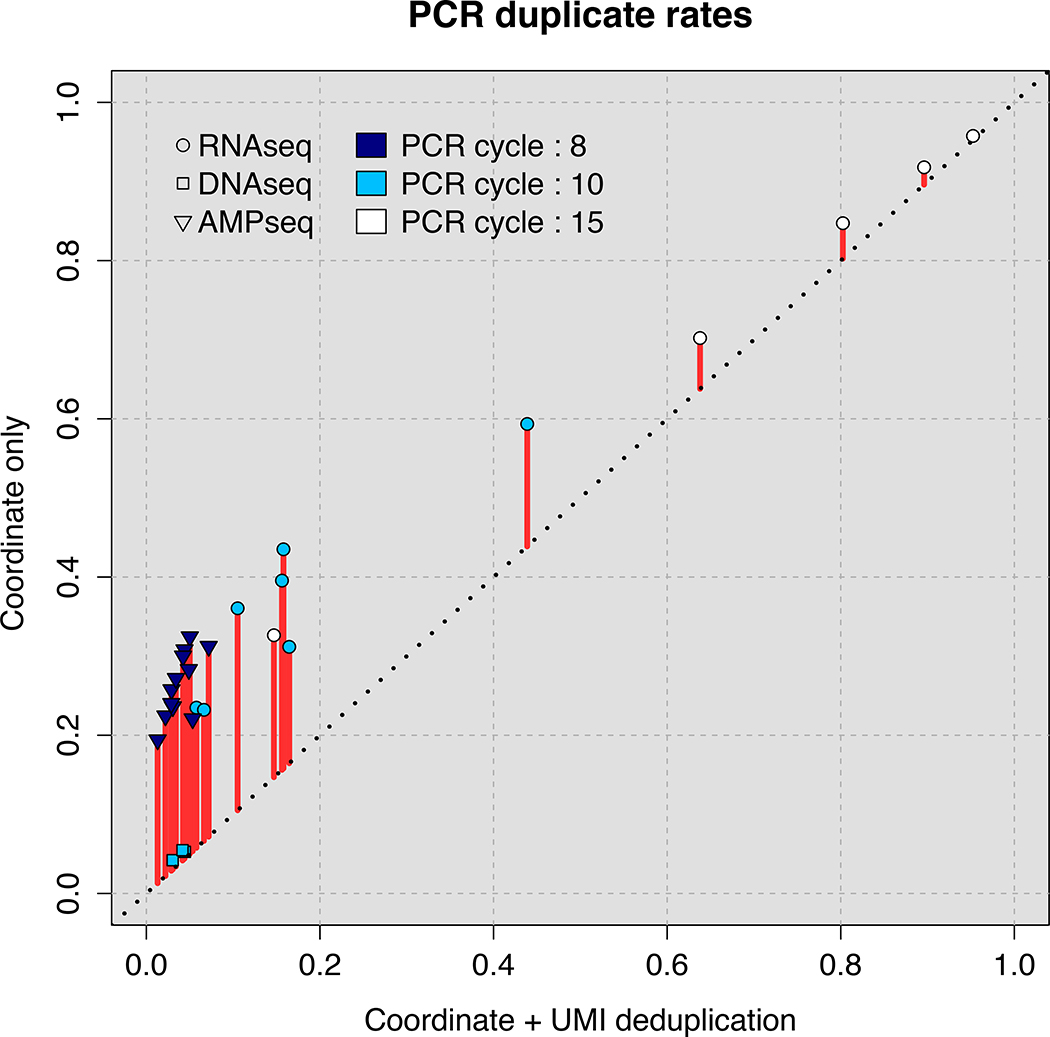
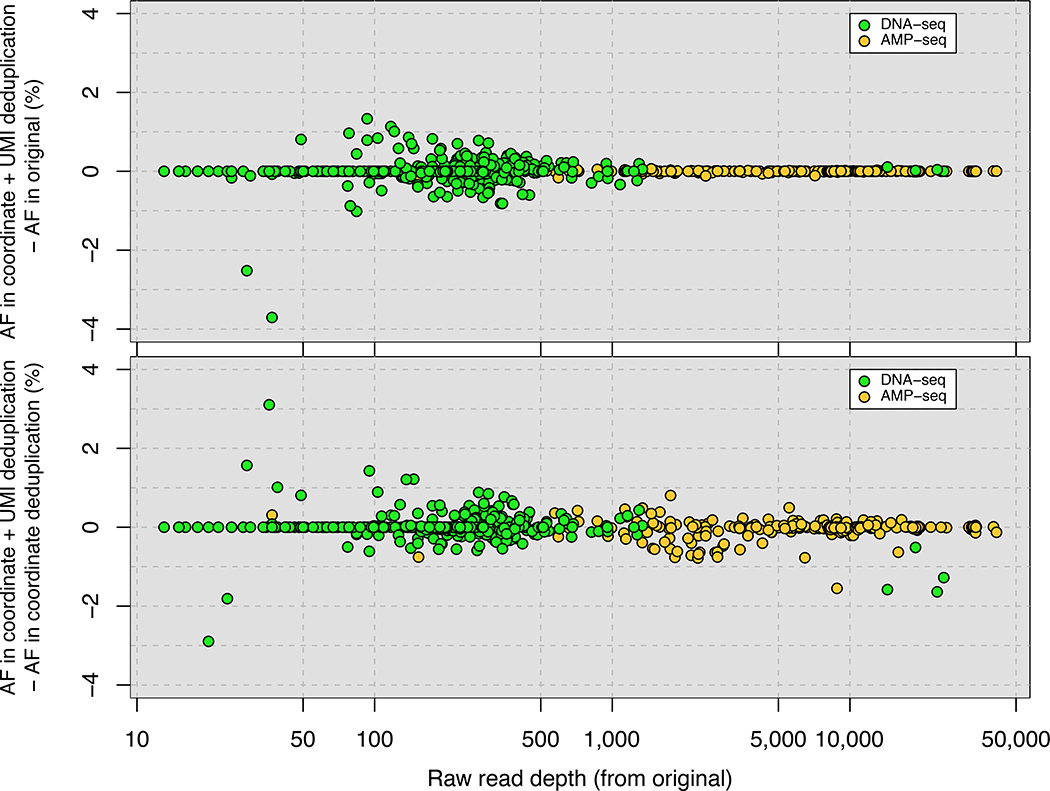
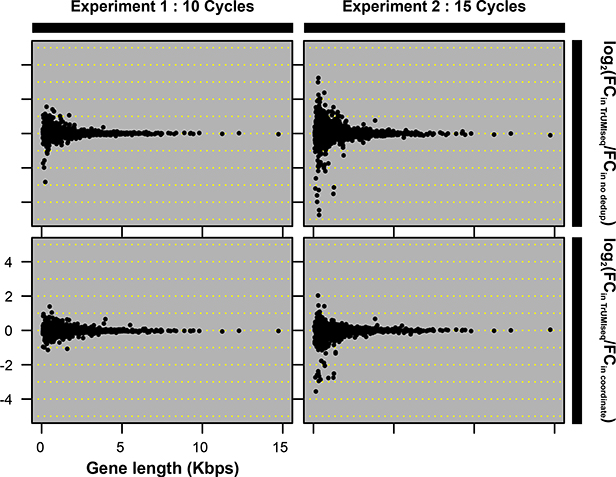
Figure 2. Accurate removal of PCR duplicates improves quantitative sequencing assays.
(A) Comparison of PCR duplicate detection rates using mapping coordinates only and mapping coordinates plus unique molecular identifiers (UMIs). (B) Differences in allele frequency (AF) estimates using deduplication based on mapping coordinates in conjunction with UMIs compared with no deduplication (upper panel) or deduplication based on mapping coordinates only (lower panel). A total of 482 (DNA-Seq) and 276 (Amp-Seq) SNPs were studied. (C) The effect of the number of PCR cycles on estimates of differential expression (DE) levels for all mRNAs using directional RNA-Seq. In each experiment, 2 biological replicates were prepared using either 10 cycles (Experiment 1) or 15 cycles (Experiment 2) of PCR. The fold change in Experiments 1 and 2 compared with 3 biological replicates of a reference sample generated using 10 PCR cycles was determined. The y-axis is the log2-transformed ratio between the fold change determined using UMI- and coordinate-based deduplication and either no deduplication (upper panel) or coordinate-only deduplication (lower panel).