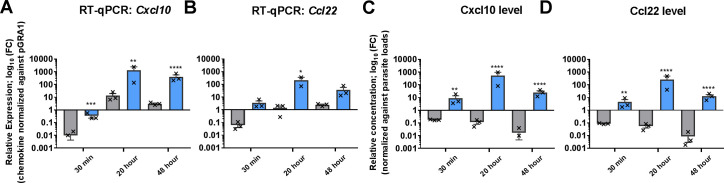
Fig 2. In vivo H. hammondi infection leads to higher levels of chemokine transcript and protein compared to T. gondii when normalized to parasite burden.
Mice were infected with T. gondii (TgVEG; grey) or H. hammondi (HhAmer; blue) or mock-infected with filter-sterilized (0.2 μm) parasite preparations. Mouse peritoneal cell RNA and their supernatants were collected at 30 min, 20 and 48 h post infection. (A-B) Bar graphs show transcript abundance (log10) normalized against parasite load (ΔCT for the host gene–ΔCT for T. gondii or H. hammondi GRA1). Cxcl10 transcript abundance normalized in this fashion was significantly higher in HhAmer-infected mice as compared to TgVEG infection at all time points (*p≤0.01) and Ccl22 transcript abundance was significantly higher in H. hammondi compared to T. gondii at 20 h post-infection (*p<0.05). (C-D) Relative concentration of secreted cytokines normalized against parasite loads. Cxcl10 and Ccl22 levels were significantly different in response to TgVEG and HhAmer infections at all time points (**p<0.01, ****p<0.0001). Error bars represent SEM.