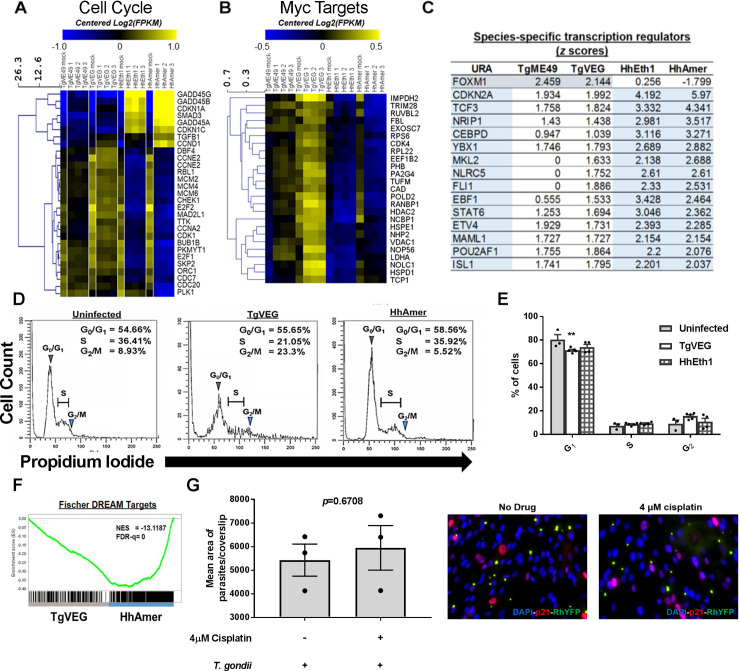
Fig 4. H. hammondi infection of THP-1 cells leads to a dramatically different impact on cell cycle regulation pathways.
(A, B) Heatmaps showing log2 transcript abundance for genes belonging to either the Cell cycle (A) or Myc targets v1 (B) gene set across strain and species. Log2 normalized data were mean-centered amongst the samples and hierarchically clustered (Euclidean distance). (C) Table showing z scores of upstream transcriptional regulators predicted to be activated (z scores ≥ 2) and/or inhibited (z scores ≤ -2; T. gondii—grey; H. hammondi–light blue) in a species-specific manner. (D) THP-1 cells were infected with T. gondii (TgVEG), H. hammondi (HhAmer) or mock-treated for 20 hours and fixed with 80% ethanol. THP-1 cells were then stained with propidium iodide (PI) and DNA content was analyzed with flow cytometry. Cell cycle progression was analyzed with ModFitLT software. Black lines represent histograms of DNA content (PI-Area) vs. cell counts. Grey arrows show the G0/G1 peaks and blue arrows mark the G2/M peak. Areas of the histogram in between the G0/G1 and the G2/M peaks contain host cells in the S phase. TgVEG-infected THP-1 cells displayed higher portions of cells found at the G2/M phase as compared to HhAmer-infected cells. (E) Cell cycle progression in U2OS cells infected with an MOI of 2 of T. gondii (TgVEG) or H. hammondi (HhEth1) was analyzed with propidium iodide (PI) staining and flow cytometry. Percentages of cells in each stage were determined with FlowJo and statistically compared using one way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test. Only T. gondii VEG-infected, and not H. hammondi American-infected, cells had a lower percentage of cells in G0/G1 compared to mock-infected cells (**P<0.01). (F) Fisher DREAM Targets gene set enrichment in H. hammondi-infected cells compared to T. gondii-infected cells. (G) Growth of T. gondii Rh-YFP on HFFs in cells treated with cisplatin to induce p21 expression (p21 levels were quantified using immunofluorescence and shown in S4C Fig). HFFs were treated with 4μM of cisplatin or vehicle for 24 h followed by infection with T. gondii Rh-YFP (MOI = 0.1). T. gondii Rh-YFP was allowed to grow for 24 h before analyzing growth of the parasites by immunofluorescence (IFA). Numbers of T. gondii RH-YFP parasites were not significantly different in cisplatin-treated HFFs as compared to mock-treated HFFs (unpaired t-test, p = 0.67).