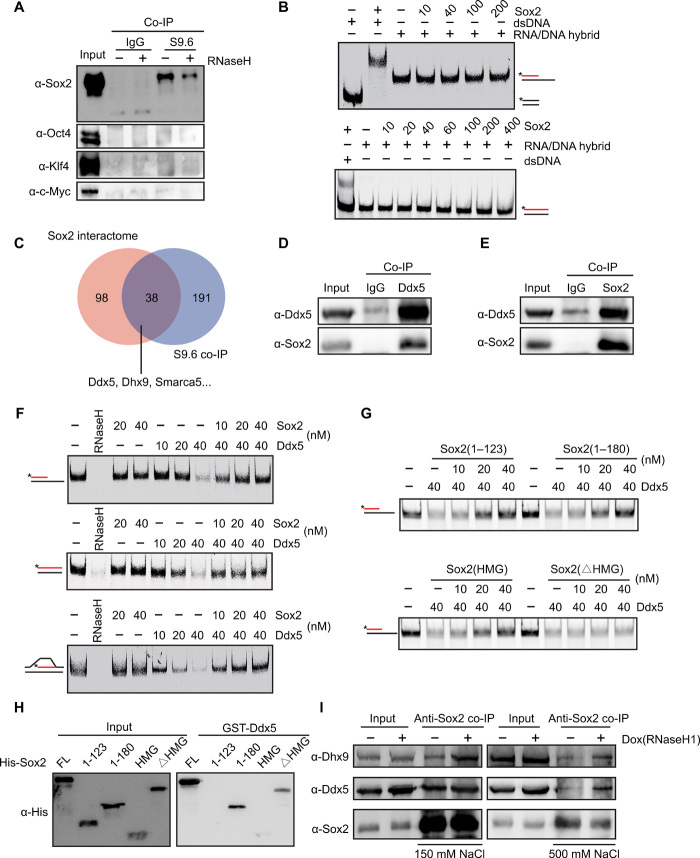
Fig. 5. Sox2 blocks the activity of Ddx5 at R-loops.
(A) Western blot to examine the interactions between Yamanaka factors and R-loop–associated complexes via S9.6 co-IP. (B) RNA/DNA + ssDNA or DNA/DNA substrate (top, 25 nM), or RNA/DNA or DNA/DNA substrate (bottom, 25 nM) with Cy5-labeled (*) RNA (red) or DNA (black) was incubated with increasing concentrations of Sox2. (C) Overlap between Sox2 interactome and RNA/DNA hybrid interactome in mESCs. (D) Co-IP to detect the interaction between Ddx5 and Sox2 in mESCs by using anti-Ddx5 antibody. (E) Co-IP to detect the interaction between Ddx5 and Sox2 in mESCs by using anti-Sox2 antibody. (F) RNA/DNA + ssDNA (top), RNA/DNA (middle), or R-loop substrate (bottom) was incubated with RNaseH, Sox2, or Ddx5 with different concentrations. (G) RNA/DNA + ssDNA substrate (25 nM) was incubated with increasing concentrations of different Sox2 deletions in the presence of Ddx5. (H) Glutathione S-transferase (GST)–pull-down analysis of the interaction between GST-Ddx5 and different Sox2 deletions. (I) Co-IP analysis of interaction between Sox2 and Ddx5 or Dhx9 in mESCs before and after inducing RNaseH1 expression by doxycycline. Experiments were performed under mild conditions (wash with 150 mM KCl) or stringent conditions (wash with 500 mM KCl). IgG, immunoglobulin G.