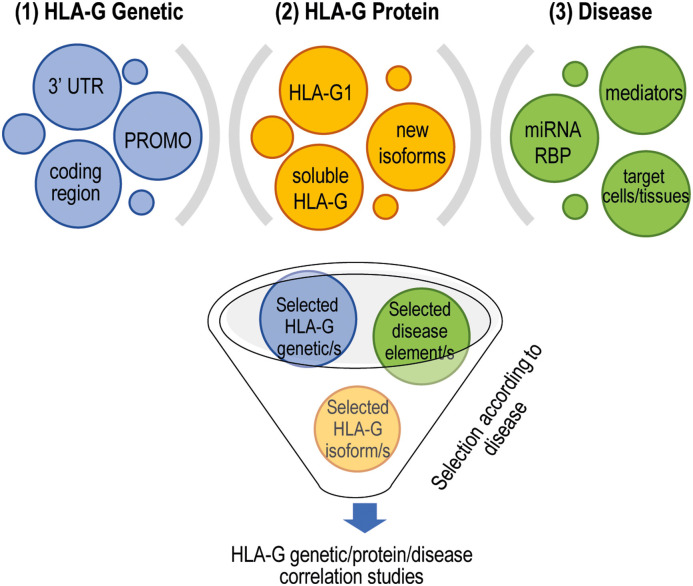
Figure 2.
Proper selection of targets to perform HLA-G genetic/protein and disease development association studies. Different layers of complexity, both cell specific and disease specific, have to be taken into account to reliably define the role of HLA-G in disease development. (1) To select the HLA-G polymorphisms to include in the analysis; (2) to include in the analysis the evaluation of disease-specific features such as the expression of specific miRNAs or RBP and the presence of proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory mediators that can modulate the expression of HLA-G, and the target cells or tissues to study that can be affected by the presence of HLA-G; (3) to identify the most appropriate HLA-G isoforms to be investigated. 3′ UTR, 3′ untranslated region; PROMO, variations in the promoter region; miRNAs, microRNAs; RBP, RNA-binding proteins.