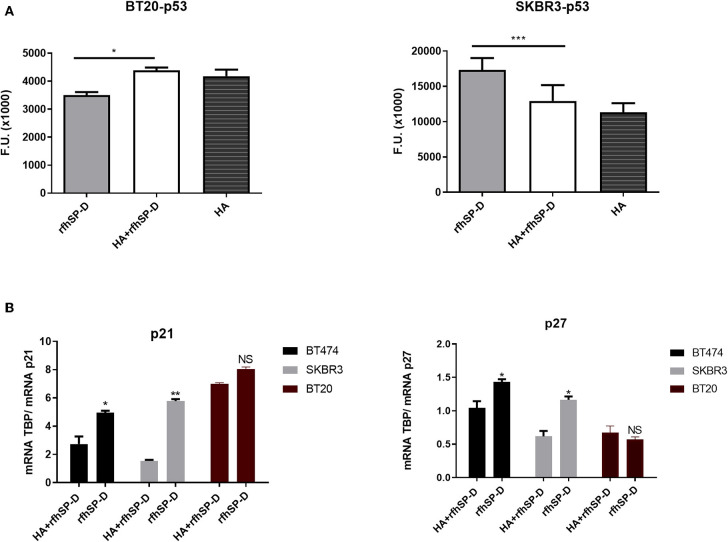
Figure 7.
Intracellular signaling to show phosphorylation of p53 in rfhSP-D-treated BT20 and SKBR3 cell lines (A). Breast cancer cell lines were allowed to adhere to HA or HA-bound rfhSP-D, and the phosphorylation status of p53 was evaluated using total cell lysates with a PathScan Antibody Array Kit (Cell Signaling). Data were generated from at least three independent experiments and presented as mean ± SD. rfhSP-D treatment resulted in upregulation of p21 and p27 cell cycle inhibitors (B). BT20, BT474, and SKBR3 (0.4 × 106) cells were seeded in a six-well-plate pre-coated with rfhSP-D and HA + rfhSP-D. The treated cells were lysed and pelleted down. The pelleted cells were subjected to RNA isolation, followed by cDNA synthesis and qPCR. The comparative quantification method was performed to calculate the efficiencies of each gene for each individual PCR and is based on the second differential maximum method or takeoff analysis. The takeoff results obtained with p21/p27 primers were normalized with the housekeeping gene TBP. qPCR assay was conducted in triplicates, and error bars represent ± SEM. Unpaired one-way ANOVA test was used to determine the significance; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 (n = 3). The statistical analysis was performed between rfhSP-D and HA + rfhSP-D-treated breast cancer cells.