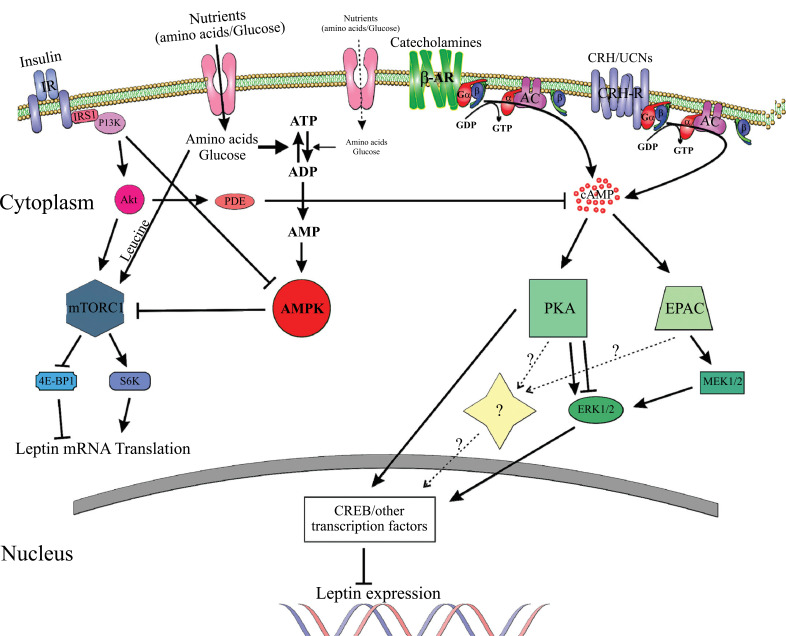
Fig. (3).
Molecular pathways involved in leptin regulation in adipocytes. 4E-BP1, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1; AC, adenylyl cyclase; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; Akt (PKB), protein kinase B; AMP, adenosine monophosphate; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; cAMP, cyclic AMP; CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein; CRH, corticotropin-releasing hormone; EPAC, guanine nucleotide exchange proteins directly activated by cAMP; ERK, extracellular-signal-regulated kinases; GDP, guanosine diphosphate; GTP, guanosine triphosphate; Gα/β/γ, G-protein alpha, beta, and gamma subunits; IR, insulin receptor; IRS1, insulin receptor substrate 1; MEK1/2, mitogen-activated protein kinase; mTORC1, mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; PDE, phosphodiesterase; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PKA, protein kinase A; S6K, p70-S6 Kinase 1; UCN, urocortin; β-AR, beta adrenergic receptor. Adapted from [38, 63, 77, 106]. For details see text. The pathway involving CRH is hypothetical and not experimentally proven.