Figure 5. Cytosolic nucleic acid‐sensing pathways involved in ionizing radiation (IR)‐induced type I interferon (IFN) signaling differ in murine and human cells.
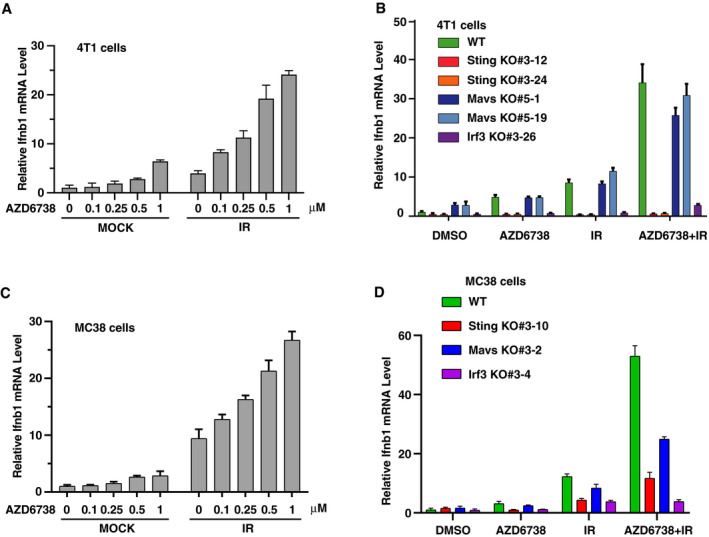
- 4T1 cells were pretreated with AZD6738 at indicated concentrations for 2 h, and then irradiated with 10 Gy. 4 days later, Ifnb1 mRNA level was measured by real‐time quantitative PCR. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean of three biological replicates.
- Same condition as described in A. Ifnb1 mRNA levels were measured by real‐time quantitative PCR in WT, Sting KO, Mavs KO, and Irf3 KO 4T1 cells. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean of three biological replicates. All KO cells were verified by immunoblotting and Sanger DNA sequencing (Appendix Fig S7).
- MC38 cells were pretreated with AZD6738 at indicated concentrations for 2 h, and then irradiated with 20 Gy. 3 days later, Ifnb1 mRNA level was measured by real‐time quantitative PCR. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean of three biological replicates.
- Same condition as described in C. Ifnb1 mRNA levels were measured by real‐time quantitative PCR in WT, Sting KO, Mavs KO, and Irf3 KO MC38 cells. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean of three biological replicates. All KO cells were verified by immunoblotting and Sanger DNA sequencing (Appendix Fig S7).
