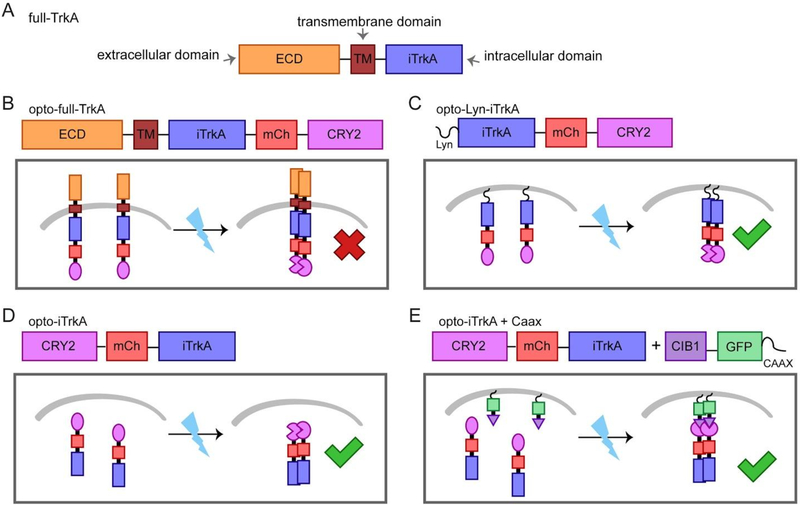
Figure 1.
Design scheme of the light-controlled TrkA systems. We have constructed four methods of optogenetic activation of TrkA signaling by fusion to CRY2. The molecular architecture of each construct is detailed. (A) The full length TrkA receptor consists of an extracellular domain (ECD), a transmembrane domain (TM) and an intracellular domain (iTrkA). (B) Opto-full-TrkA is a fusion of CRY2 to the C-terminus of full length TrkA. (C) Opto-Lyn-iTrkA appends CRY2 to the C-terminal end of the intracellular domain of TrkA (iTrkA), and features an N-terminal Lyn membrane-targeting sequence. (D) Opto-iTrkA fuses CRY2 to the N-terminus of iTrkA. (E) Opto-iTrkA + CAAX uses CIBN-CAAX, localized to the plasma membrane, in combination with opto-iTrkA to recruit iTrkA to the membrane in a light-dependent manner.