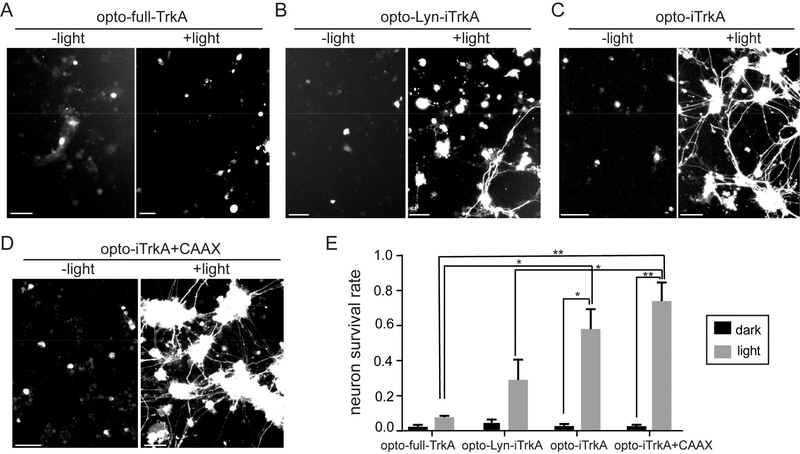
Figure 4.
Light-induced TrkA activation supports DRG neuron survival in the absence of NGF. After transfection, primary rat DRG neurons were allowed to recover in NGF-supplemented medium for 24 h. Then, NGF was withdrawn and replaced with anti-NGF for 48 h while the cultures were subjected to continuous blue light stimulation at 200 μW/cm2 or kept in dark for 2 days. (A) DRG neurons transfected with opto-full-TrkA and GFP did not survive under light or dark. (B) Some DRG neurons expressing opto-Lyn-iTrkA and GFP survived upon blue light stimulation, but few survived in the dark control. (C) Many DRG cells expressing opto-iTrkA survived and had extended long axons upon blue light stimulation, but not in the dark controls. (D) Most DRG neurons expressing opto-iTrkA and CIB1-GFP-CAAX were alive with long axons with blue light, but not in the dark controls. (E) Quantification of survival rate of DRG neurons for optoTrkA systems, in light and dark conditions. Results are averaged from three independent sets of experiments (see numbers of cells in each set of experiment in Table S2) and presented as means ± SEM. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test was performed between cells with different transfection. t test was performed between cells in dark or in light with the same transfection (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.005). Scale bars, 50 μm.