FIGURE 1.
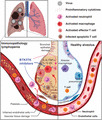
Potential of BTK/ITK inhibitors for attenuating immunopathology and lymphopenia in COVID-19. SARS-CoV-2 infection in the lungs set off proinflammatory cytokine production by lung cells and immune cells such as macrophages and neutrophils. Cytokine release syndrome further engages pulmonary and vascular tissue damages, leukocyte recruitment, T cell activation, and other cytotoxic immune responses. T cells are possible targets of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Infected and over reactive T cells may be prompted toward apoptosis and cytolysis, resulting in infection-induced lymphopenia. BTK/ITK inhibitors may function to down-regulate proinflammatory cytokine production by innate immune populations and reduce cytotoxic T cell death while sustaining virus-specific effector T cell function, therefore exhibit therapeutic functions against immunopathology and lymphopenia. Solid-line arrows indicate known functions and dashed-line arrows indicate functions awaiting investigation
