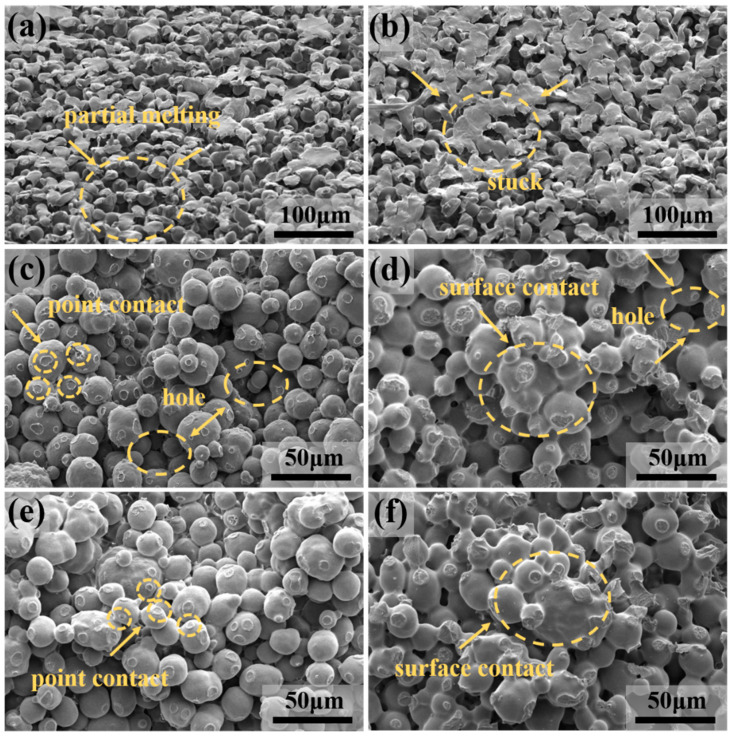
Figure 3.
The microstructure of the sample under different sintering temperatures: (a,b) Surface microstructure of sample under the molding condition of rotary sintering at 170 °C and 200 °C, respectively, where the arrows indicate the melting of samples; (c,d) cross-sectional microstructure of sample under the molding condition of static sintering at 170 °C and 200 °C, respectively, with the charging amount of 3 g; (e,f) cross-sectional microstructure of sample under the molding condition of rotary sintering at 170 °C and 200 °C, respectively, with the charging amount of 4 g. Arrows in (c–f) indicate the melting and the contact mode between the particles and the difference in porous structure of samples obtained by rotary and static sintering methods.