FIGURE 1.
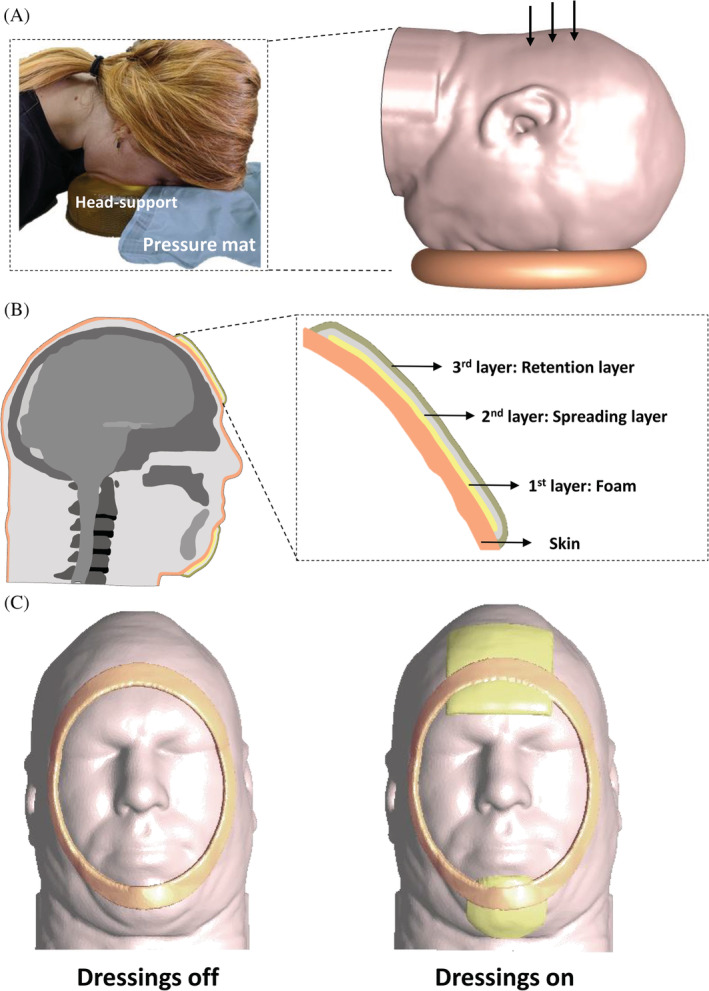
The model geometry and determination of boundary conditions: A, The three‐dimensional (3D) anatomically‐accurate computational finite element (FE) model of an adult head in a prone surgical or intensive care position. The frame on the left‐hand side documents measurements of facial interface pressures when the head of a prone subject is positioned on a donut‐shaped headrest. B, Mid‐sagittal cross‐section through the 3D FE head model with magnification to visualise the structure of the multi‐layered Mepilex Border Flex dressing (Mölnlycke Health Care, Gothenburg, Sweden) which is simulated to be applied prophylactically here, to protect the forehead (in the magnified cross‐section) and chin. C, Inferior views of the 3D FE head model when positioned on the donut‐shaped headrest with the applied forehead and chin dressings (right frame) and without dressings (left frame). The contours of the head support are also shown in both cases, for clarity
