Fig 1.
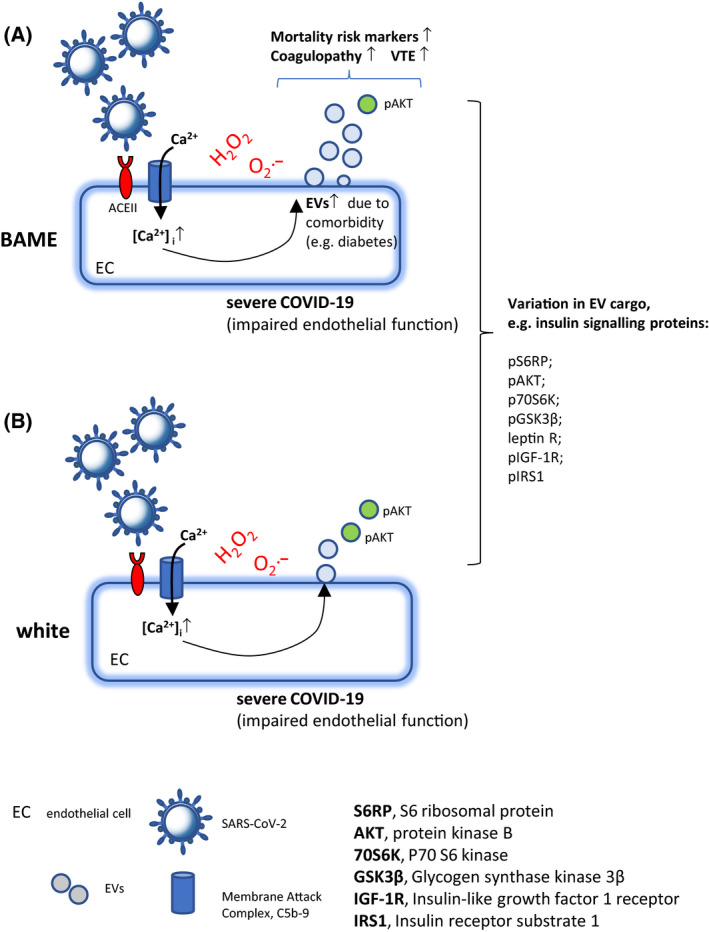
(A and B) Extracellular vesicles (EVs) and coagulopathy in COVID‐19 and a possible link with ethnicity. SARS‐CoV‐2 infection activates the complement and formation of membrane attack complex (MAC, C5b‐9). The resulting Ca2+ influx through deposited C5b‐9 and by the SARS‐CoV‐2 E‐protein Ca2+ channel from Endoplasmic reticulum‐Golgi intermediate compartment/endoplasmic reticulum (ERGIC/ER), leads to Ca2+‐mediated EV release. Circulating EVs carrying phosphorylated insulin signalling proteins and related to diabetes mellitus, an important comorbidity in COVID‐19, are associated with clinical mortality risk markers linked to ethnicity. (A) In severe COVID‐19, in particular in ethnicities with increased comorbidities such as diabetes, and associated circulating EV levels, EVs with their known role in coagulopathy could play an important role in COVID‐19‐related deaths through VTE. BAME. Black Asian and Minority Ethnic groups.
