Fig. 5 |. TET proteins promote super bivalent H3K4me3 in E6.5 Epi.
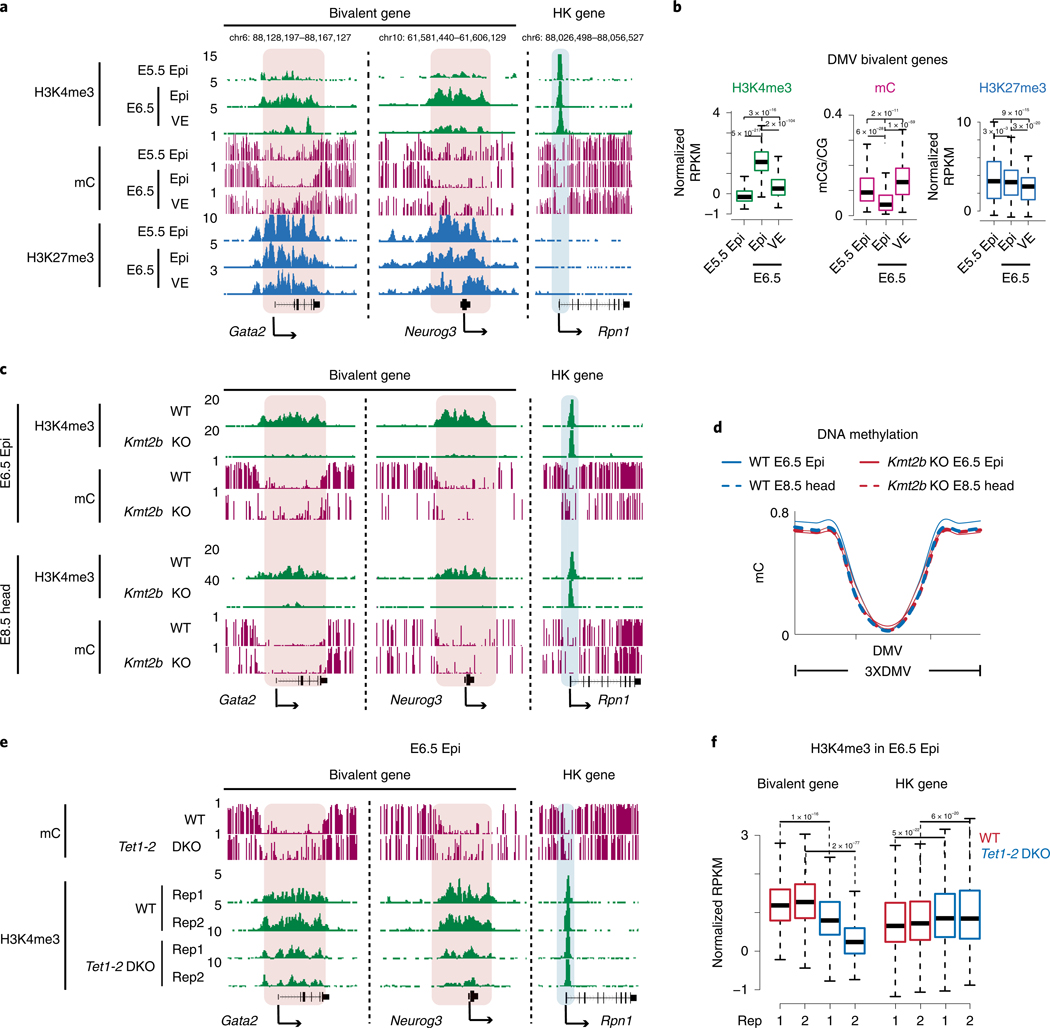
a, Snapshots showing H3K4me3, DNA methylation34 and H3K27me3 enrichment at two developmental genes Gata2 and Neurog3, and a housekeeping gene Rpn1 in E5.5 Epi (n = 2), E6.5 Epi (n = 2) and E6.5 VE (n = 2). The genome browser view scales were adjusted on the basis of the global data range. b, Boxplots showing H3K4me3, DNA methylation and H3K27me3 enrichment at DMVs in E5.5 Epi, E6.5 Epi and E6.5 VE. The median of each dataset is indicated by the center line. The bottom, top edges and whiskers represent the 25th and 75th percentiles and 1.5 times the IQR, respectively. The P values were calculated by two-sided t-test. c, Snapshots showing H3K4me3 and DNA methylation in WT and Kmt2b−/− E6.5 Epi (n = 3) and E8.5 head (n = 2). The genome browser view scales were adjusted on the basis of the global data range. d, Metaplots showing DNA methylation of DMVs at bivalent genes between WT and Kmt2b−/− E6.5 Epi or E8.5 head. e, Snapshots showing DNA methylation34 and H3K4me3 enrichment in WT and Tet1/2 DKO E6.5 Epi (n = 2). The genome browser view scales were adjusted on the basis of the global data range. f, Boxplots showing H3K4me3 for DMV bivalent genes and housekeeping genes between WT (n = 2) and Tet1/2 double knockout (n = 2) E6.5 Epi. The median of each dataset is indicated by the center line. The bottom, top edges and whiskers represent the 25th and 75th percentiles and 1.5 times the IQR, respectively. The P values were calculated by a two-sided t-test.
