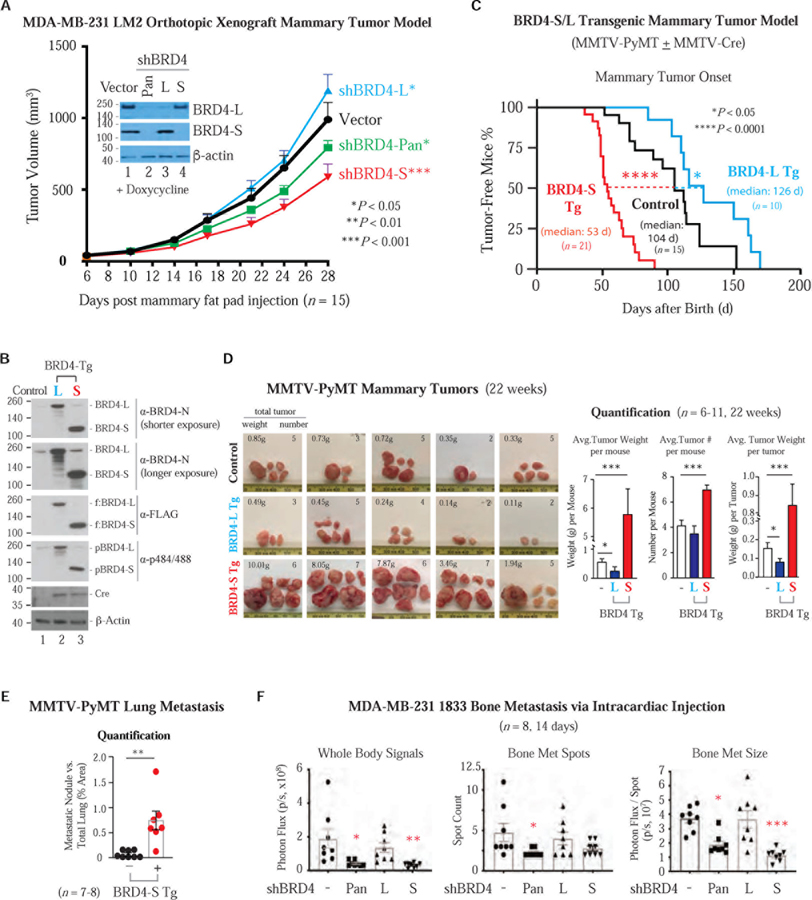
Figure 2. BRD4-S Enhances Mammary Tumor Growth and Metastasis While BRD4-L Suppresses Mainly Tumor Growth.
(A) Orthotopic mammary tumor growth of MDA-MB-231 LM2 cells expressing doxy-inducible BRD4 shRNA or vector. IB shows the extent of BRD4 knockdown prior to mammary fat pad injection. Data are mean ± s.e.m. P, two-way ANOVA.
(B) IB shows Cre-induced FLAG-tagged BRD4-S/L transgene (Tg) expression in MMTV-PyMT mammary tumors. Control, no Cre.
(C) Percentage of tumor-free mice with palpable mammary tumor onset in immunocompetent syngeneic mice expressing BRD4 Tg isoforms and in control mice without MMTV-Cre expression. P, Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test.
(D) PyMT tumor images (left) and quantification of average tumor weight/number (right). Data are mean ± s.e.m. P, two-tailed t-test.
(E) Quantification of lung metastatic nodules from female mice bearing PyMT tumors with or without (control) BRD4-S Tg. Data are mean ± s.e.m. P, two-tailed t-test.
(F) BLI quantification of bone metastasis from MDA-MB-231-derived 1833 lines harboring doxy-induced BRD4 pan or isoform shRNA. Bone metastatic size is signal intensity per spot. Data are mean ± s.e.m. P, two-way ANOVA.