Figure 1.
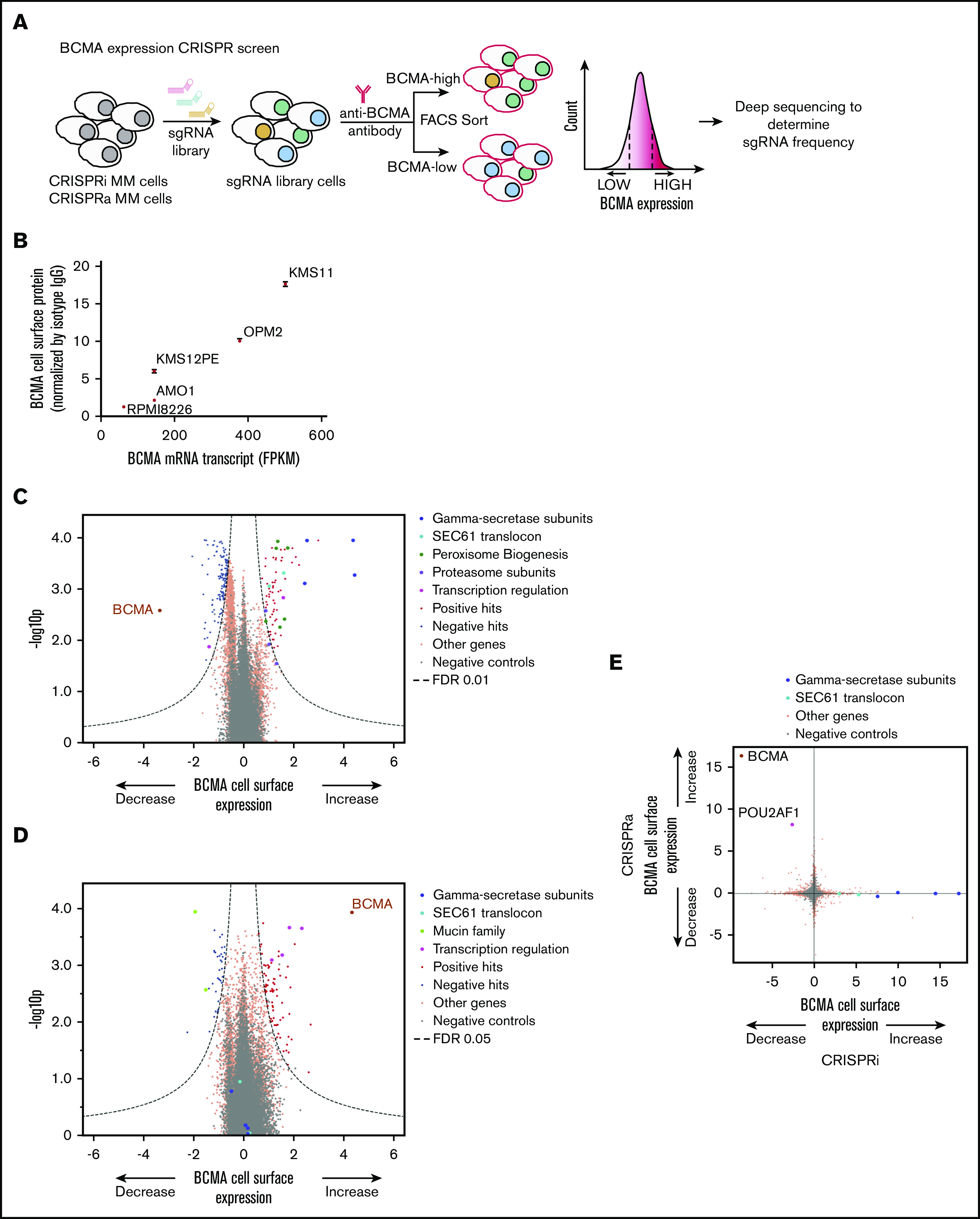
Genome-wide CRISPRi/CRISPRa screens to identify genes regulating cell surface expression of BCMA. (A) Schematic representation of our genome-wide CRISPRi and CRISPRa screens to identify modulators of BCMA expression. AMO1 cells constitutively expressing the CRISPRi or CRISPRa machinery were transduced with a genome-wide lentiviral sgRNA library. After transduction, cells were stained for cell surface levels of BCMA and sorted by FACS to enrich for populations with low or high levels of cell surface BCMA. Frequencies of cells expressing a given sgRNA were determined in each population by using next-generation sequencing. (B) BCMA expression levels in a panel of MM cell lines. BCMA transcript FPKM levels obtained from the Keats Laboratory database (https://www.keatslab.org) were plotted against cell surface expression levels of BCMA quantified according to flow cytometry. The flow cytometry data are the means of 3 biological replicates, and error bars denote standard deviations. Note that some error bars are not visible because values are small. Volcano plots indicating the BCMA expression phenotype and statistical significance for knockdown (CRISPRi) (C) or overexpression (CRISPRa) (D) of human genes (orange dots) and quasi-genes generated from negative control sgRNA (gray dots). Hit genes corresponding to functional categories are color-coded as labeled in the panel. (E) Comparison of phenotypes from the CRISPRi and CRISPRa screens. Selected hit genes are color-coded. IgG, immunoglobulin G; mRNA, messenger RNA.
