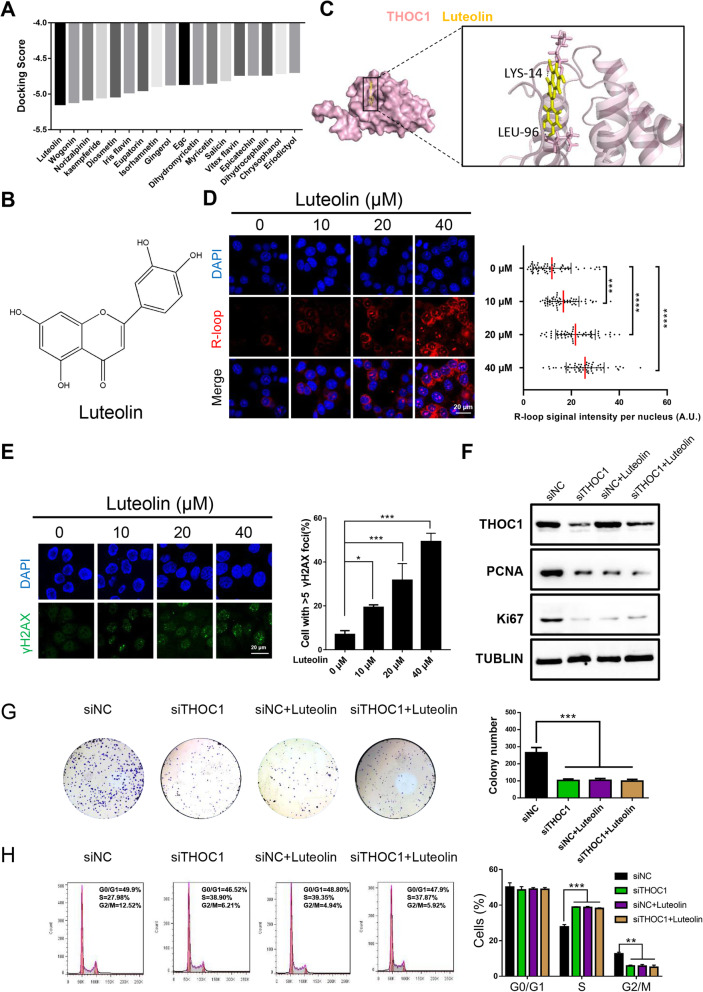
Fig. 5.
Luteolin reduces HCC proliferation by targeting THOC1 in vitro. a Molecular docking results of THOC1 with multiple traditional Chinese medicine. b Molecular structure of luteolin. c Image of molecular dynamics simulation visualizes the combination of luteolin with THOC1. d Immunostaining with R-loop (red) in PLC/PRF/5 cells treated with different concentrations of luteolin (0, 10, 20, and 40 μM) for 48 h. Median of the R-loop signal intensity per nucleus after nucleolar signal removal is shown (one-way ANOVA; ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001). Scale bar, 20 μm. e Immunofluorescence of γH2AX (green) in PLC/PRF/5 cells treated with different concentrations of luteolin (0, 10, 20, and 40 μM) for 48 h. Percentage of cells that contain > 5 γH2AX foci is shown (one-way ANOVA; *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001). Scale bar, 20 μm. f THOC1 and the proliferation marker (PCNA and Ki67) expressions in PLC/PRF/5 cells transfected with siNC and siTHOC1 plasmids, followed by separate treatment with DMSO or luteolin (20 μM) for 48 h. g Colony formation and (h) cell cycle assays in PLC/PRF/5 cells transfected with siNC and siTHOC1, followed by separate treatment with DMSO or luteolin (20 μM) for 48 h. The numbers of colonies and proportion of cell cycle phases were compared (one-way ANOVA; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001)