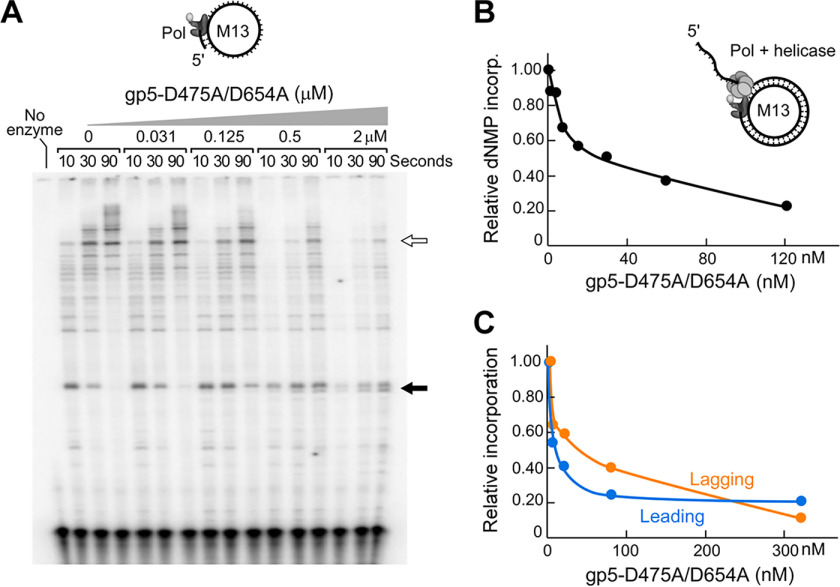
Figure 4.
Inhibition of WT T7 DNA polymerase by gp5-D475A/D654A. A, gp5-D475A/D654A inhibits primer extension by T7 DNA polymerase. A 32P-5′-end-labeled primer (50 nm) was annealed to M13 ssDNA (10 nm) and incubated with 100 nm WT T7 DNA polymerase, in the presence of 0.3 mm dNTPs, and increasing concentrations (0.03, 0.13 0.5, or 2 μm) of gp5-D475A/D654A. Samples were removed at 10, 30, and 90 s after addition of MgCl2 and separated on a denaturing polyacrylamide gel. Examples of extension intermediates accumulating (black arrow) or decreasing (white arrow) as the concentration of gp5-D475A/D654A increases. B, inhibition of strand-displacement DNA synthesis by gp5-D475A/D654A. Strand-displacement reactions rely on the helicase activity of gp4 to displace dsDNA encountered during DNA synthesis by T7 DNA polymerase. The reaction mixtures were supplemented with gp5-D475A/D654A (0, 1.9, 3.8, 7.5, 15, 30, or 120 nm). The samples were incubated for 5 min at 30 °C after initiating the reaction by addition of MgCl2 and quenched with 50 mm EDTA, and the incorporation of dGMP was measured by liquid scintillation counting. C, gp5-D475A/D654A inhibits coordinated leading and lagging-strand DNA synthesis. gp5-D475A/D654A (0, 5, 20, 80, or 320 nm) was incubated in a standard minicircle reaction (see “Experimental Procedures”) for 5 min prior to addition of MgCl2. The reactions were incubated at 30 °C for 5 min and quenched with 50 mm EDTA, and incorporation of dGMP (for leading strand synthesis) or dCMP (for lagging-strand synthesis) was measured by liquid scintillation counting.