Figure 1.
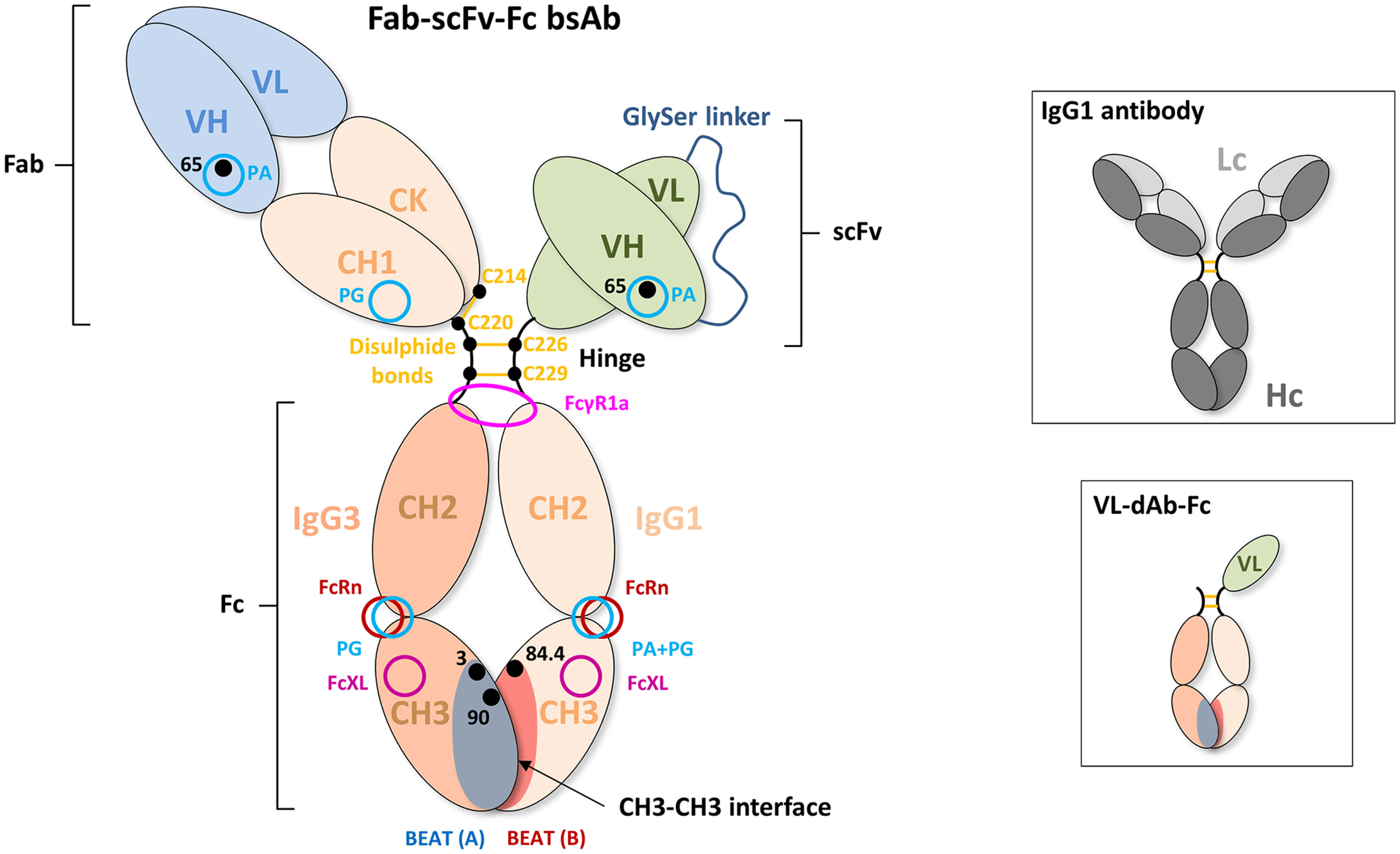
Schematic drawing of a Fab–scFv–Fc bsAb. The first Hc noncovalently interacts with the second Hc via the CH3 domains that form the CH3–CH3 interface. Mutations that promote Hc HD, such as those composing the BEAT interface, are generally found in this portion of the antibody. The CH3 domains are connected to the CH2 domains, which together form the antibody Fc portion. The purification resins PA and PG bind at the interface between the CH2 and CH3 domains of the human IgG1 isotype. PA does not bind the IgG3 isotype. The FcRn receptor (neonatal Fc receptor), which promotes long serum half-life, also binds at the CH2–CH3 interface. The CH2 domains are connected to the hinge region. The hinge consists of the lower, middle, and upper hinge, wherein the lower hinge is coded by the CH2 exon. FcγR1a binds asymmetrically across the N-terminal region of the CH2 domains and lower hinge. The middle hinge of the IgG1 isotype contains two cysteine residues (Cys226 and Cys229) that form intermolecular disulfide bonds with the same cysteines of the second Hc. The N terminus of the upper hinge is connected to the CH1 domain followed by the VH domain. The CH1 domain interacts noncovalently with the constant domain of the Lc, which is termed constant κ (CK) or constant λ (Cλ), depending on the class of Lc. An intermolecular disulfide bond is formed between Hc and Lc, as shown here between Cys220 of the upper hinge of the IgG1 isotype and Cys214 of the CΚ domain. The VH domain interacts noncovalently with the VL domain. The CH1 domain contains a PG-binding site, and VH domains of the VH3 subclass contain a PA-binding site. PA binding in VH domains of the VH3 subclass can be abrogated using the G65S mutation. To circumvent Lc mispairing, one of the Fab domains can be converted into a scFv by genetic fusion of the VH domain to the VL domain via a flexible linker (generally (Gly4-Ser)3). The resulting domain is then fused to the hinge region. In the case of the VL–dAb–Fc format (inset), a VL-dAb is fused directly to the N terminus of the hinge of one of the Hcs. Cysteine residues are numbered according to the Eu numbering system, VH residues are numbered according to the Kabat numbering system, and CH3 residues are numbered according to IMGT.
